| Battle of Shipu | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Sino-French War | |||||||
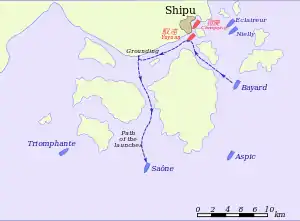 Map of the battle | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
2 ironclads 3 cruisers 1 gunboat |
3 cruisers 1 frigate 1 sloop | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 1 killed |
1 frigate sunk 1 sloop sunk by friendly fire | ||||||
The Battle of Shipu (Chinese: 石浦海戰) was a French naval victory during the Sino-French War (August 1884–April 1885). The battle took place on the night of 14 February 1885 in Shipu Bay (石浦灣), near Ningbo, China.
Background
The battle arose from an attempt by part of the Chinese Nanyang Fleet (Southern Seas fleet) to relieve the French blockade of Formosa (Taiwan). On 18 January 1885 the Chinese cruisers Nan Chen, Nanrui (南瑞) and Kaiji (開濟) left Shanghai, accompanied by the frigate Yuyuen and the composite sloop Chengqing (澄慶), and sailed towards Formosa. The Chinese flotilla was under the command of Admiral Wu Ankang (吳安康). The Nanyang ships were originally to have been accompanied by Chaoyong (超勇) and Yangwei, two relatively modern cruisers from the Beiyang Fleet, under the command of the German 'guest-admiral' Siebelin, but Li Hongzhang diverted these two Beiyang ships to Korean waters. (Tension between China and Japan over Korea was running high at the period, following Yuan Shikai's defeat of the Gapsin Coup in December 1884.)
According to L. C. Arlington, an American naval officer serving as a 'foreign adviser' aboard the frigate Yuyuen, the sortie was made in a mood of deep despondency. The Chinese captains had no confidence in their ability to meet the French in combat and were determined to avoid battle if they possibly could. The Chinese flotilla sailed south slowly and hesitantly, never out of sight of land, and with frequent halts to exercise the ships' guns. Before the flotilla reached the Taiwan strait Admiral Wu had already despaired of completing his mission. He proposed instead merely to announce that the Chinese flotilla was on its way to Formosa, in the hope that this false rumour would force the French to raise the blockade of Formosa and concentrate their warships for defence. The Chinese flotilla turned around and headed back to Sanmen Bay, close to the Chinese port of Ningbo.[1]
The Chinese sortie was duly reported in the Hong Kong newspapers at the end of January 1885. Captain Baux of Triomphante, who had been stationed in Hong Kong to monitor the news from China, immediately cabled the news to Admiral Amédée Courbet at Keelung. The French, weary of the monotonous routine of the blockade and frustrated with their inability to get to grips with the Chinese, jumped at the chance of destroying half the Nanyang Fleet at sea. Courbet sailed north from Keelung in early February to hunt down the Chinese with the ironclads Bayard and Triomphante, the cruisers Nielly, Éclaireur and Duguay-Trouin, the gunboat Aspic and the troopship Saône.
The chase

Uncertain where to find the enemy, Courbet first looked into the mouth of the Min River (7 February), then headed northwards along the China Coast.[2]
On 9 February, with supplies of coal beginning to run short on some ships, Courbet was obliged to send the cruiser Duguay-Trouin back to Keelung.[3]
On 10 February the rest of the French squadron reached the Chusan Islands and on 11 February entered the mouth of the Yangzi River, to the alarm of the Chinese batteries at Wusong. There was still no sign of the Chinese. Eventually the French established communications with the shore and combed the Chinese newspapers for the latest news of the sortie. They discovered that the Far East Squadron had passed the Chinese cruisers on its voyage north, and that the enemy vessels were now lurking in Sanmen Bay. Courbet immediately headed southwards, and led the squadron at night through the hazardous passages of the Chusan Islands to close with the enemy as soon as possible. On 13 February, off Shipu Bay (Sheipoo Bay, as it was then known by Europeans), to the south of the Chusan Islands, Éclaireur caught sight of the Chinese flotilla and signalled 'Five steamships in view to the south'.
The French squadron immediately offered battle, and bore down on the Chinese. The Chinese flotilla initially advanced against the French in a 'V' formation, led by Admiral Wu's flagship Kaiji, and for one brief, exhilarating moment the French believed that the Chinese had accepted battle. They had no doubt that they would destroy the Chinese ships with ease. Suddenly, however, before the range closed, the enemy flotilla broke its formation and scattered. The three cruisers headed south, pursued by Courbet's squadron, while Yuyuen and Chengqing took refuge in Shipu Bay. According to Arlington, Admiral Wu had a grudge against the captains of these two ships, and deliberately sacrificed them in order to save the rest of the Chinese flotilla.
Courbet's ships were unable to catch the faster Chinese cruisers, and on the evening of 13 February Courbet took his squadron back to Shipu Bay to deal with Yuyuen and Chengqing.
The battle


On the night of 14 February the French attacked the Chinese ships with two torpedo launches, commanded respectively by capitaine de frégate Palma Gourdon and lieutenant de vaisseau Émile Duboc. Both men had already distinguished themselves in the early battles of the Tonkin campaign. Gourdon had been one of the first officers into the Vietnamese defences at the Battle of Thuận An (20 August 1883), and Duboc had fought heroically at the Battle of Paper Bridge (19 May 1883) and the Battle of Phủ Hoài (15 August 1883).
The two French officers timed their attack to coincide with the start of the Chinese Lunar New Year festival, in the hope of catching the Chinese off their guard. The bay was also full of junks and sampans which had taken refuge there from the French, and Duboc and Gourdon hoped that their small launches, painted black for camouflage, could mingle with these vessels and approach their targets unseen. (Arlington had warned the Chinese captains to clear these small boats away from the two Chinese warships, but his advice had been ignored.) The two French launches, under cover of darkness, managed to approach to within 100 metres (330 ft) of their targets without being seen. But the Chinese sentries on both ships were on the alert, and the French launches were spotted some distance away from their objectives. Under heavy Chinese rifle fire, Duboc and Gourdon made an extremely dangerous approach and successfully exploded their spar torpedoes against Yuyuen's hull, crippling the Chinese frigate. Both launches then made their escape from Shipu Bay and were recovered the following morning by Saône. One French sailor was killed by rifle fire during the attack.[5]
Arlington has left a valuable description of the battle from the Chinese viewpoint. He was aboard Yuyuen when the frigate was attacked by the two French launches, and described vividly the panic that ensued after the explosion of the spar torpedoes, as the Chinese crewmen abandoned ship and swam for the shore. During the confusion of the French attack the Chinese shore batteries opened fire. The Chinese artillery fire was wildly inaccurate and at least one shell seems to have hit the composite sloop Chengqing, crippling her also:
The scene that now occurred almost beggars description. Some tried to lower the boats, some rushed between decks to try and save their possessions, many jumped overboard into the sea. It was, in fact, everyone for himself, and the devil take the hindmost. When I had time to realise what had really happened, a strange scene was unrolled before me. Just ahead of us lay the little Ching-ching slowly settling down beneath the waters; she had been attacked by the same torpedo boat that had sunk us. Our own ship was gradually sinking, her guns just level with the water's edge. Along the shore and in the water about us were seamen, soldiers, chickens, ducks, geese and baggage of every description. The fault rested entirely with the Chinese—even at the last moment, had they made any attempt to repel the torpedo boat they might have warded off the catastrophe, and possibly sunk the enemy instead. No such attempt was made, and the French escaped scot-free.[6]
On the morning of 15 February the French scouted Shipu Bay and discovered that both Chinese ships had been sunk. Gourdon and Duboc were feted on their return to the French squadron, and were both decorated for the heroism they had shown in pressing home their torpedo attack under fire.
Embarrassed by the loss of one of their ships to friendly fire, the Chinese authorities later claimed that Chengqing had been deliberately scuttled to prevent her from falling into the hands of the French. However, both Arlington and Duboc record seeing a bright flash and hearing a loud explosion aboard Chengqing during the battle. Arlington assumed that the sloop had been struck by a French torpedo, but she seems rather to have fallen victim to a Chinese shell. Duboc and Gourdon were insistent that they had only attacked Yuyuen, not Chengqing.
French warships in the Shipu expedition

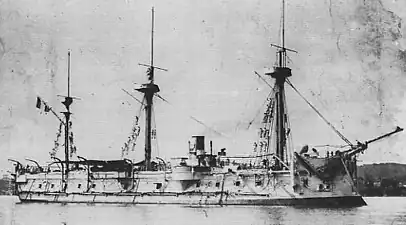 Triomphante
Triomphante Duguay-Trouin
Duguay-Trouin_img_2590.jpg.webp) Éclaireur (scale model on display at Toulon naval museum)
Éclaireur (scale model on display at Toulon naval museum)
Notes
References
- Arlington, L. C., Through the Dragon's Eyes (London, 1931)
- De Lonlay, D., L'amiral Courbet et le « Bayard »; récits, souvenirs historiques (Paris, 1886)
- Duboc, E., Trente cinq mois de campagne en Chine, au Tonkin (Paris, 1899)
- Huard, L., La guerre du Tonkin (Paris, 1887)
- Loir, M., L'escadre de l'amiral Courbet (Paris, 1886)
- Lung Chang [龍章], Yueh-nan yu Chung-fa chan-cheng [越南與中法戰爭, Vietnam and the Sino-French War] (Taipei, 1993)
- Randier, J., La Royale (La Falaise, 2006) ISBN 2352610222
- Rawlinson, J., China's Struggle for Naval Development, 1839–1895 (Harvard, 1967)
- Thomazi, A., La conquête de l'Indochine (Paris, 1934)
- Wright, R., The Chinese Steam Navy, 1862–1945 (London, 2001)
