 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
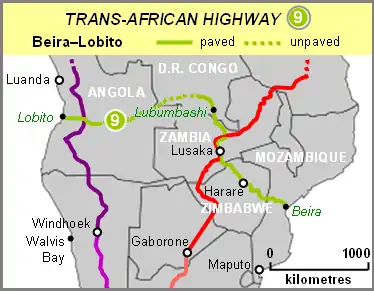 | ||||
| Route information | ||||
| Length | 3,523 km (2,189 mi) | |||
| Major junctions | ||||
| East end | Beira, Mozambique | |||
| West end | Lobito, Angola | |||
| Location | ||||
| Highway system | ||||
| ||||
| ||||
The Beira–Lobito Highway or TAH 9 is Trans-African Highway 9 in the transcontinental road network being developed by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA), the African Development Bank (ADB), and the African Union. The route has a length of 3,523 km (2,189 mi) crossing Angola, the most southerly part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and central Mozambique.
The route links mining areas of DR Congo, Zambia and Zimbabwe and agricultural production areas of Angola, Zambia and Zimbabwe to the Atlantic port of Lobito and Indian Ocean port of Beira. Civil wars in Angola, DR Congo, Zimbabwe and Mozambique have affected development of the highway in the past, most recently in DR Congo and Angola, both still in a rebuilding phase.
The route is also served by a rail link running parallel to it for much of its length except between Kafue and Harare, though it too has been damaged in wars and its western half, the Benguela Railway, does not currently operate.
Between Kapiri Mposhi and Kafue in Zambia, the highway shares the route with the Cairo-Cape Town Highway.
When complete the highway will be the southernmost of the Trans-African network's east-west crossings of the continent. However regional highways developed by the Southern African Development Community (SADC) already offer well-functioning and fully paved alternative routes, particularly the Trans-Kalahari Corridor and Maputo Corridor from the port of Walvis Bay in Namibia via Botswana and South Africa to the port of Maputo in southern Mozambique.
Furthermore Zambia has completed the Barotse Floodplain causeway (the Mongu–Kalabo road),[1] extending its Lusaka-Mongu Road, and has proposed to the Angolan government that it continue into that country to link up with its road network via Kalabo and Sikongo.[2] Secondly, DR Congo has been offered a loan and construction assistance by China to develop a railway from Lubumbashi to its port of Matadi as its main trade route.[3] Trans-African Highway 9 might then be relegated to a back-burner by Southern African regional developments.
Route
The entire route from Lobito to Beira is 3523 kilometres.
Angola
It starts in Lobito, Angola (north-east of Benguela), as part of the EN100 Route. After a few kilometres north-east, it becomes the EN250 Route eastwards. It is the EN250 Route for the remainder of the Angolan Section, through Cuíto, to Luau, Moxico Province, where it crosses the Kasai River Borderline into the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DR Congo) and the town of Dilolo. At the junction with the EN120 in the town of Alto Hama, the Beira–Lobito Highway intersects with the Tripoli-Cape Town Highway (Trans-African Highway 3). The Angolan Section is 1160 kilometres.
DR Congo
From Dilolo, it goes eastwards as the N39 route, through Kolwezi, to the town of Guba (north of Likasi), where it becomes part of the N1 Route south-eastwards. It is the N1 Route for the remainder of the DR Congo Section, through Likasi and Lubumbashi, to the border town of Kasumbalesa (DR Congo) in the Copperbelt Region, where it crosses the near borderline into the Republic of Zambia and the border town of Kasumbalesa (Zambia). The DR Congo Section is 830 kilometres.
Zambia
From Kasumbalesa, it goes southwards as the T3 Route, through Chingola, Kitwe and Ndola to exit the Copperbelt Region and reach the town of Kapiri Mposhi, where it becomes part of the T2 Route, Zambia's Great North Road. It is the T2 Route for the remainder of the Zambian Section, through Kabwe and Lusaka (Zambia's Capital City), to the border town of Chirundu (Zambia), where it crosses the Zambezi River as the Chirundu Bridge into the Republic of Zimbabwe and the border town of Chirundu (Zimbabwe). From Kapiri Mposhi to the T1 Route junction after Kafue (50 kilometres south of Lusaka), the Beira–Lobito Highway shares its route with the Cairo-Cape Town Highway (Trans-African Highway 4). The Zambian Section is 610 kilometres.
Zimbabwe
From Chirundu, it goes south-east as the R3 Highway (A1 Highway) to the city of Harare (Zimbabwe's Capital City), where it becomes the R5 Highway (A3 Highway) south-east to the city of Mutare, where it passes through various suburbs using various roads and crosses the Machipanda Border Post into the Republic of Mozambique and the border town of Machipanda. The Zimbabwean Section is 625 kilometres.
Mozambique
From Machipanda, it goes eastwards as the N6 Route, through Manica and Chimoio, to end in the city of Beira. The Mozambican Section is 300 kilometres.
Developments
In 2023, the governments of Zambia, DR Congo and Angola agreed to declare the section of the route from Ndola in Zambia's Copperbelt Province, through DR Congo and Angola to Lobito as a trade corridor (the Lobito Corridor) in order to link the landlocked Copperbelt Region with its closest ocean (the Atlantic Ocean) for trade,[4] as Zambia and DR Congo are two large producers of both copper and cobalt.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ "Zambia : The Mongu-Kalabo road has been completed". 2016-04-08. Retrieved 2023-04-12.
- ↑ Sifukwe, Hector (4 November 2021). "Zambia, Angola to be linked by road - Milupi". ZNBC. Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ↑ International2007-10-07T03:51:00, Railway Gazette. "Chinese to plug Ilebo - Kinshasa gap in DR Congo". Railway Gazette International. Retrieved 2023-04-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - 1 2 "Angola, Zambia, Congo Set Up Joint Agency to Manage Key Trade Corridor". Bloomberg.com. 2023-01-31. Retrieved 2023-07-08.
- African Development Bank/United Nations Economic Commission For Africa: "Review of the Implementation Status of the Trans African Highways and the Missing Links: Volume 2: Description of Corridors". August 14, 2003. Retrieved 14 July 2007.
- Michelin Motoring and Tourist Map: "Africa North and West". Michelin Travel Publications, Paris, 2000.
