A binary system is a system of two astronomical bodies of the same kind that are comparable in size. Definitions vary, but typically require the center of mass to be located outside of either object. (See animated examples.)
The most common kinds of binary system are binary stars and binary asteroids, but brown dwarfs, planets, neutron stars, black holes and galaxies can also form binaries.
A multiple system is similar but consists of three or more objects, for example trinary stars and trinary asteroids.
Classification
In a binary system, the brighter or more massive object is referred to as primary, and the other the secondary.
Binary stars are also classified based on orbit. Wide binaries are objects with orbits that keep them apart from one another. They evolve separately and have very little effect on each other. Close binaries are close to each other and are able to transfer mass from one another. They can also be classified based on how we observe them. Visual binaries are two stars separated enough that they can be disinguished through binoculars or a small telescope.
Eclipsing binaries are where the objects' orbits are at an angle that when one passes in front of the other it causes an eclipse, as seen from Earth.
Astrometric binaries are objects that seem to move around nothing as their companion object cannot be identified, it can only be inferred. The companion object may not be bright enough or may be hidden in the glare from the primary object.
A related classification though not a binary system is optical binary, which refers to objects that are so close together in the sky that they appear to be a binary system, but are not. Such objects merely appear to be close together, but lie at different distances from the Solar System.[1][2]
Binary companion (minor planets)
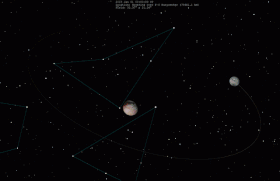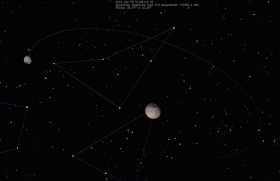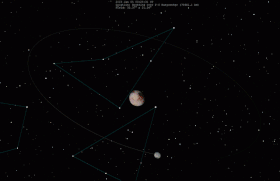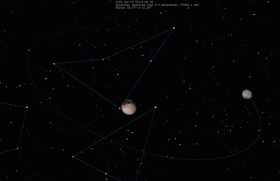
When binary minor planets are similar in size, they may be called "binary companions" instead of referring to the smaller body as a satellite.[3] Good examples of true binary companions are the 90 Antiope and the 79360 Sila–Nunam systems. Pluto and its largest moon Charon are sometimes described as a binary system because the barycenter (center of mass) of the two objects is not inside either of them, but Charon is small enough compared to Pluto that it is usually classified as a moon.[4] The Sun and Jupiter orbit a point outside of either, but are not considered a binary because they are different kinds of objects.
See also
References
- ↑ "Binary Star Systems: Classification and Evolution". Space.com.
- ↑ Lehmann, Holger. Analysis of Spectroscopic Binaries. Thüringer Landessternwarte Tautenburg.
- ↑ "Satellites and Companions of Minor Planets". IAU / Minor Planet Center. 2009-09-17. Archived from the original on 2011-01-21. Retrieved 2011-01-08.
- ↑ Ian O'Neill (8 August 2014). "Can We Call Pluto and Charon a 'Binary Planet' Yet?". Discovery News. Retrieved 15 July 2015.
External links
Bibliography
- Astronomy: A Visual Guide by Mark A. Garlick