 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
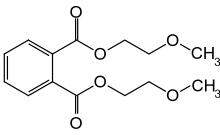
| IUPAC name
Bis(2-methoxyethyl) phthalate | |
| Other names
Di(2-methoxyethyl) phthalate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.830 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H18O6 | |
| Molar mass | 282.292 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.170 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | −55 °C (−67 °F; 218 K) |
| 0.85% w/w[2] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[3] | |
 | |
| H360FD | |
| P201, P202, P280, P308+P313, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | ~200 °C |
| 390 °C (734 °F; 663 K) | |
| Explosive limits | Lower explosion limit: 0.3 % |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
Dermal - Rabbit - 19,800 mg/kg |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
10 mg/m3 STEL) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Bis(2-methoxyethyl) phthalate, also commonly di(2-methoxyethyl) phthalate (DMEP), is a phthalate ester baring 2-methoxyethanol groups. Historically it was used as a plasticizer in cellulose acetate plastics, it is now largely banned owing to concerns over its effects to human health.
References
- ↑ Hayashi, Sadao; Sawayama, Isamu; Motoyama, Takuhiko (1963). "Synthesis of Glycol Ester Plasticizers and their Effects on Polyvinyl Acetate". Journal of Japan Oil Chemists' Society. 12 (2): 102–104. doi:10.5650/jos1956.12.102.
- ↑ Ritchie, Patrick Dunbar (1972). Plasticisers, stabilisers and fillers;. London: Iliffe Books for the Plastics Institute. p. 134. ISBN 0592054454.
- ↑ Sigma-Aldrich Co., Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate. Retrieved on 2022-05-12.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.