Blake River Megacaldera Complex | |
|---|---|
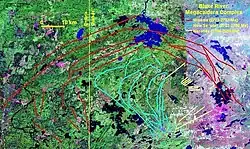 Map of the Blake River Megacaldera Complex. Misema Caldera is highlighted in red, New Senator Caldera in cyan and Noranda Caldera in pale yellow. | |
| Coordinates: 48°20′05″N 79°16′20″W / 48.334744°N 79.272093°W | |
| Location | Ontario-Quebec, Canada |
| Range | Canadian Shield |
| Age | 2,706 million years ago |
| Volcanic arc/belt | Abitibi greenstone belt |
| Last eruption | 2,696 million years ago |
The Blake River Megacaldera Complex is a giant subaqueous caldera cluster or a nested caldera system that spans across the Ontario–Quebec border in Canada.
The caldera complex is around 2.7 billion years old, consisting of a series of overlapping calderas of various ages and sizes. It lies within the southern zone of the Abitibi greenstone belt of the Superior Craton and has an area of 3,000 km2 (1,200 sq mi).
The Blake River Megacaldera Complex has been a centre of major interest since 2006 with numerous excursions at the international, national and local level.[1] It is a world-class metallotect with respect to both hydrothermal Cu-Zn massive sulfides and gold-rich massive sulfides.
Structure and geographical extent
The Blake River Megacaldera Complex consists of mainly mafic to intermediate volcanic flows and less abundant felsic volcanic flows and intercalated pyroclastic rocks, which underwent three stages of major volcanic activity.
- The first phase resulted in the creation of the 80 km (50 mi) long, 40 km (25 mi) wide, east-west striking Misema Caldera which has been dated to 2704–2707 Ma. It is a coalescence of at least two large mafic shield volcanoes that formed more than 2703 million years ago.
- The second phase resulted in the creation of the 30 km (19 mi) long, 15 km (9.3 mi) wide, northwest–southeast trending New Senator Caldera which formed 2701–2704 Ma. Its formation consists of thick massive mafic sequences which has inferred to be a subaqueous lava lake during the early stages of the caldera's development.[1]
- The third phase of activity constructed the classic east-northeast striking 2696 Ma Noranda Caldera which contains a 7-to-9-km-thick succession of mafic and felsic rocks erupted during five major series of activity.[1]
The Blake River Megacaldera Complex is considered a supervolcano due to its great size and its multiple dikes and vents. The Misema Caldera is in the order of 3,500 to 4,000 km2 (1,400 to 1,500 sq mi), making the complex similar to the Yellowstone Caldera in Wyoming, Lake Toba in Indonesia and strikingly similar in structure to the Olympus Mons caldera on Mars.[2] As a result, the Blake River Group is best categorized as a meganested caldera complex.[3]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 ASH FALL: Newsletter of the Volcanology and Igneous Petrology Division Geological Association of Canada Retrieved on 2007-09-21
- ↑ Montréal 2006 – Technical Program Archived 2011-07-06 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 2007-11-02
- ↑ Blake River Group evolution: characteristics of the subaqueous Misema and New Senator calderas Archived 2011-07-06 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 2008-01-23