| Bothriocline longipes | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Genus: | Bothriocline |
| Species: | B. longipes |
| Binomial name | |
| Bothriocline longipes | |
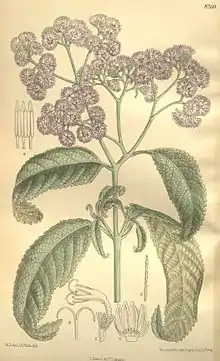
Bothriocline longipes is a woody perennial herb or shrub capable of reaching three meters tall. It is part of the family Asteraceae.
Description
Woody herb or shrub, leaves, opposite, petiole is up to 2.5 cm long; leaf-blade is narrowly ovate with an acute apex and a base that is cuneate to rounded. Flowers, corolla is lilac, mauve or bright purple colored [1]
Chemistry
Compounds isolated from the flowers of the species shows the presence of anthocyanidins.[2] Oil extracted from the seed of Bothriocline longipes was identified to contain non epoxy tri-glycerides and epoxy acids.[3]
Uses
Extracts of the species are used as ingredients of a regimen of herbal remedies to treat a variety of pain or inflammatory related issues. Leaf extracts are used in managing colic pains, diarrhea, syphilis and conjunctivitis.[4] Parts of root is chewed to ameliorate sore throat.[5]
References
- ↑ Beentje, Hank (2000). Flora of Tropical East Africa - Compositae 1 (2000). Henk Beentje. Rotterdam: A.A. Balkema. p. 148. ISBN 90-6191-395-0. OCLC 45341200.
- ↑ Adaku, Christopher; Skaar, Irene; Berland, Helge; Byamukama, Robert; Jordheim, Monica; Andersen, Øyvind M. (2019-02-01). "Anthocyanins from mauve flowers of Erlangea tomentosa (Bothriocline longipes) based on erlangidin – The first reported natural anthocyanidin with C-ring methoxylation". Phytochemistry Letters. 29: 225–230. doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2018.12.016. ISSN 1874-3900. S2CID 104448752.
- ↑ Phillips, B. E.; Smith, C. R.; Hagemann, J. W. (1969). "Glyceride structure ofErlangea tomentosa seed oil, a new source of vernolic acid". Lipids. 4 (6): 473–477. doi:10.1007/BF02531027. ISSN 0024-4201. PMID 5367929. S2CID 4049593.
- ↑ Muhwana, Isaac; Obakiro, Samuel Baker; Ibanda, Ivan; Crucifix, Pender Gift; Afodun, Adam Moyosore; Odoma, Saidi (2020-05-22). "Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of the aqueous leaf extract of Erlangea tomentosa (Asteraceae) in rats and mice". Journal of Pharmacy & Bioresources. 17 (1): 19–23. doi:10.4314/jpb.v17i1.4. ISSN 0189-8442.
- ↑ Glover, P. E.; Stewart, Joyce; Gwynne, M. D. (1966). "Masai and Kipsigis Notes on East African Plants: Part III—Medicinal Uses of Plants". East African Agricultural and Forestry Journal. 32 (2): 200–207. doi:10.1080/00128325.1966.11662117. ISSN 0012-8325.