| Brachyphalangy | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Brachyphalangism |
 | |
| Brachyphalangy of the thumb's distal phalanx, also known as brachydactyly type D, with otherwise normal phalanges of the 2nd-5th digits | |
| Symptoms | Having a phalange(s) shorter than average |
| Usual onset | Birth |
| Duration | Life-long |
| Frequency | Exact frequency not known, but brachyphalangy is considered to be rare |
Brachyphalangy is a condition in which one or more of the phalanges of the fingers and toes are smaller than normal.[1]
This condition is one of the most common non-syndromic causes of brachydactyly and clinodactyly.
Causes
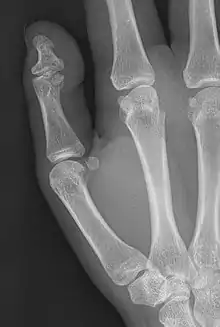
Brachyphalangy of the distal phalange of the thumb
This condition is caused by either fusion or early closure of the phalange's growth plate. One example is brachydactyly type D, which is caused by an early closure of the thumb's distal phalange, leading to a congenitally short thumb with a similarly short and wide thumb nail.
References
- ↑ "brachyphalangia". The Free Dictionary. Retrieved 29 May 2022.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.