 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Tribromoacetaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.698 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
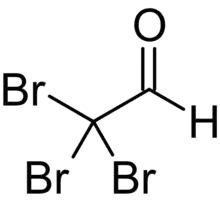
| C2HBr3O | |
| Molar mass | 280.741 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Oily liquid |
| Melting point | −57.5 °C (−71.5 °F; 215.7 K) |
| Boiling point | 174 °C (345 °F; 447 K) |
| Reacts to form bromal hydrate | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Toxic |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H301, H310, H314 | |
| P260, P262, P264, P270, P280, P301+P316, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P302+P361+P354, P304+P340, P305+P354+P338, P316, P321, P330, P361+P364, P363, P405, P501 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
100 mg/kg (rat, oral)[2] 25 mg/kg (mice, oral)[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Fluoral, Chloral, Iodal |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Bromal (tribromoacetaldehyde) is a brominated aldehyde. It reacts with water to form bromal hydrate.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "Tribromoacetaldehyde". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- 1 2 "Initial Submission: Acute Toxicity Studies of Tribromoacetaldehyde with Cover Letter dated 09/21/92". Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC. Office of Toxic. 1992.
- ↑ Novak, A.; Whalley, E. (January 1960). "Infrared spectra of fluoral, chloral and bromal hydrates". Spectrochimica Acta. 16 (5): 521–527. Bibcode:1960AcSpe..16..521N. doi:10.1016/0371-1951(60)80008-2.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.