Bryan Money is a term used by numismatists to refer to tokens and medals associated with William Jennings Bryan's platform during the United States presidential elections of 1896 and 1900.[1] Bryan's platform advocated for the reinstatement of silver currency in the United States economy as part of the short-lived Silver Republican Party.
In the wake of the panic of 1893 came the dawn of the upcoming presidential campaign. Farm prices collapsed, banks failed, unemployment was at 20%, and the economy was stalled. The money supply was backed by gold. The government could not print more greenbacks without gold backing. The protectionists wanted high tariffs to keep out foreign goods and create jobs in the United States.
The Populist Party's remedy was to substantially increase the money supply by adopting a dual monetary standard. With the acceptance of silver as an additional backer, more money could be printed. The United States had vast silver deposits in reserve as well as in the ground, waiting to be mined. The working man supported this addition of silver. These issues polarized the people of the west and south on one side and the northeast on the other, farmer against the industrialist, the well-to-do against the lower economic classes.
Candidates need an issue or platform upon which to sell themselves. For the elections of 1896 and 1900, Bryan chose the issue of the standard by which the government backed its currency - either with just gold or his choice of both silver and gold. Supported by both the National Silver Party and the Populist Party, Bryan, a Democrat from Nebraska, ran unsuccessfully against William McKinley of Ohio in both those races.
The Silverites referred to the inscription used on the edge of the first silver dollars, 1794-1804, "HUNDRED CENTS ONE DOLLAR OR UNIT" as evidence that the intentions were to have the silver dollar a unit of measure. Bryan expounded the free coinage of silver using the ratio, 16 oz. of silver = 1 oz. of gold. Free coinage of silver means a person could bring silver ingots to the United States Mint and have them coined. For example, $0.53 of silver would produce a silver dollar, which is what the Morgan dollar (1878-1921) contained. If the government issued dollars containing 100 cents worth of silver, they would have been very large and cumbersome.
Bryan's opponents quickly exaggerated the size of this coin and made base metal caricature or satirical pieces produced in lead type metal, zinc, Babbitt metal, tin, bronze, aluminum, iron and other combinations. Some were as large as approximately 8 inches. The level of quality of the Bryan Money was controlled by the individual ability of each craftsman (see example).
Tradesmen groomed in the nineteenth century had various talents. The makers of Bryan Money were printers, blacksmiths, tool and die makers, hardware people, foundry workers, dentists and any handy person bursting with political opinion. There also were thousands produced and sold for profit by the manufacturers of novelties. Affluent jewelers in the east, such as Tiffany & Co., made several different coin silver comparative pieces (see example). They showed the outline of the Morgan dollar in comparison to the larger full content dollar. Also shown were the date, fineness of silver, and the rate of exchange of 16 to 1.



Political context
Following the demonetization of silver, dubbed the "Crime of ‘73", tensions arose between factions of both the Democratic and Republican political parties. Some wished to maintain a single gold standard, while others advocated for a bi-metal standard in which silver would be valued at a rate of 16 ounces for every ounce of gold. During the 1896 and 1900 elections, Bryan, along with several lesser parties, argued for a dual standard because it would enable the government to put more paper money into circulation, as it could be backed by both gold and silver.[1] His opponent William McKinley's platform preserved the gold standard. McKinley's supporters issued Bryan Money as a political statement about these dueling standards.
Types of Bryan Money
Bryan Money falls into two categories: comparative and satirical. Comparative tokens were made of coin silver by true silversmiths. Their main purpose was to compare the size and ratio of silver needed for dual standard currency to silver's market price. These pieces were modeled after the silver dollar format and were later banned due to counterfeiting concerns.[1]
Satirical tokens bore "derisive or humorous inscriptions" that mocked the proposed dual standard.[1] Many pieces had similar slogans such as "In God We Trust for the Other 47 Cents" and "16 to 1 NIT" (Not In Trust), referring to the proposed value ratio of silver to gold.[2] These pieces were more often cast or struck and made of type metal or alloys of lead and aluminum. Other designs were made of less typical materials such as iron, copper, tin or cardboard.[1] After the design's initial production, individual craftsmen would often copy them in a crude fashion and distribute them to fellow supporters, contributing to the variety of quality of Bryan Monies.
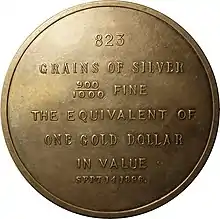
Collecting Bryan Money
Bryan Money was never intended for circulation and was rarely carried so it was spared the normal wear of other collectible currency. Most imperfections consist of rim bumps and scratches from accidental damage or graffiti. Grading by third parties and an interest in so-called dollars increased the value of many Bryan pieces.[3]
Bryan Money designs were also used in other collectibles. These included "Campaign Bills" in which the designs were printed on material similar to paper money, and silk fabrics with embroidered designs that were used for neckties and other purposes.[1]
Coin collectors had little interest in Bryan Money in the late 1800s because it was not a true currency, but rather political commentary. Farran Zerbe raised awareness of the tokens' collectible nature when he published his definitive catalog, Bryan Money: Tokens of the Presidential Campaigns of 1896 and 1900 - Comparative and Satirical, in the July 1926 volume of The Numismatist. Now, due to its political relevance, both numismatists and collectors of political memorabilia take interest in Bryan Money.[3]
Zerbe's article captured what makes Bryan Money distinctive from other collectible currency:
- "Bryan Money is unique as a series. The monetary-political issue, conditions and temperament of the time, and the tolerance of disregard for the letter of the law, all being in favorable conjunction, made possible what never before or may never again occur - such a large and interesting variety of grotesque political satires in metal."[1]
Today, Bryan Money is cataloged by Schornstein Number (SCH) in accordance with the Token and Medal Society (TAMS) 2001 publication Bryan Money and the 2012 Bryan Money Supplement and Price Guide, both by Fred Schornstein.
Footnotes
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Zerbe, Farran (July 1926). "Bryan Money: Tokens of the Presidential Campaigns of 1896 and 1900 - Comparative and Satirical". The Numismatist. 39 (7): 313–315.
- ↑ Peterson, Norman G. (December 1997). "Bryan Money". TAMS Journal. 37 (6): 199.
- 1 2 Schornstein, Fred (July 2012). "Bryan Money: Supplement and Price Guide 2012". TAMS Journal. 52 (4:2): 4.
Further reading
- Fred Schornstein, Bryan Money. Lake Mary, FL: Token and Medal Society, 2001.
- Farran Zerbe, "Bryan Money", The Numismatist, vol. 39, no. 7 (July 1926).
- Farran Zerbe, Bryan Money: Tokens of the Presidential Campaigns of 1896 and 1900, Comparative and Satirical. N.C.: N.P., 1961.