
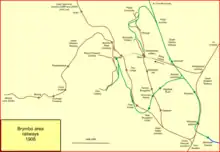
The Brymbo railway branch lines served the rich reserves of coal, iron, limestone and other minerals in an area around Brymbo to the west of Wrexham in Wales. Coalowners and others needed transport to get their products to market and lines were built from the main line into the mineral-bearing area. The topography was difficult and gradients were steep. The Great Western Railway became dominant, but a rival company built a competing line and branches.
Brymbo was surrounded by a maze of duplicating branch lines serving pits and quarries and a passenger service was started on some routes. Brymbo became the centre of a considerable iron and steelmaking activity but the industry declined before World War II and in the 1960s it reduced considerably. The passenger service was discontinued, and mineral traffic declined as its customers ceased to trade. There is no railway in the area at the present day.
North Wales Mineral Railway
The North Wales Coalfield runs from near Talacre at the mouth of the River Dee through Wrexham to Oswestry. The coal and associated iron industries became active from the early-eighteenth century, but poor transport links to markets suppressed the potential of the trade. The North Wales Mineral Railway (NWMR) was promoted locally to connect pits and ironworks to Chester and wharves on the River Dee. Its title signified the intent, but differences with pit owners meant that connections to pits were not included in the Parliamentary Bill. The North Wales Mineral Railway obtained the Royal Assent to its Act of Incorporation on 6 August 1844, for a line from Wrexham to a river wharf at Saltney, and a junction with the Chester and Holyhead Railway at Saltney, was authorised in the same session. The C&HR connection gave access to Chester.
An extension to Ruabon was authorised on 21 July 1845, and the Act included a branch from Wheatsheaf, north of Wrexham, to Brymbo and Minera. A third Act on 27 July 1846, authorised short branches to collieries at Ffrwd,[note 1] Brynmally, Brymbo and Vron.[1]
On to Shrewsbury
The Chester and Holyhead Railway announced its intention to build a line from Chester to Shrewsbury, the Cheshire and Shrewsbury Junction Railway. It would abstract a large proportion of the NWMR's income, and to counter the threat, the NWMR devised its own scheme to extend the NWMR southwards, the Shrewsbury, Oswestry and Chester Junction Railway which was authorised on 30 June 1845. The Cheshire and Shropshire Junction scheme was rejected. The NWMR and the Shrewsbury, Oswestry and Chester Junction Railway together formed a through route and a year later, authorised by Act of Parliament on 7 July 1846 they merged as the Shrewsbury and Chester Railway.[2]
Lines opened
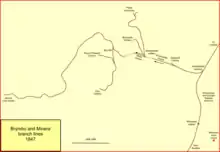
The main line from Ruabon to Saltney opened on 4 November 1846; the Company got access to Chester over a short section of the Chester and Holyhead Railway; this section opened on the same day; there were five passenger trains each way daily. Opening on to Shrewsbury followed in 1848.
The branch line from Wheatsheaf through Brymbo to Minera was open in July 1847 and the other local branches, to pits at Gwersyllt and Broughton, were ready and open in November 1847. Together these connected a large number of pits and works, and the large lime deposits of Minera, to the railway network.[2][3]
Boyd later adds that "two small branches off it ran to Brynmally and Ffrwd, opening in the November [1847]: in due time Westminster, Southsea, Brymbo and Vron Collieries were also rail served off the Minera Branch.[4]
The line left the NWMR main line near an inn called the Wheatsheaf, and the junction took that name; not far from the junction the line climbed an inclined plane, called the Wheatsheaf or Summerhill Incline, at a gradient of 1 in 15. The section was operated on the balance system. At the head of the incline the line passed through a Summerhill Tunnel, 200 yards long. Now at the lower end of the Moss Valley, the line ran to the next incline, the Moss or Cerni incline, gradient 1 in 4. This was also a balanced incline. At the head of this incline the line entered Brymbo Tunnel, 396 yards, and soon reached the Brymbo Iron Works, operated by the Brymbo Mineral and Railway Company from 3 October 1842.[note 2][5]
At first horse traction, and gravity, were used on the line, but a small locomotive is reported to have been brought in later, generally operating from Brymbo to Minera.[6]
LNWR branch line
In 1849 the Mold Railway opened, from near Chester to Mold. A branch line was opened at the same time, from Mold to Ffrith, where there were pits near the margin of the coalfield. The terrain was extremely difficult and the line had steep gradients. The Mold Railway was in the camp of the London and North Western Railway, and that company thereby had its first foothold in the area.[7]
Wrexham and Minera Railway
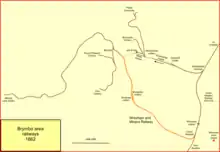
The earlier (1847) branch from Wheatsheaf Junction to Minera via Brymbo was difficult to work, having two rope-worked inclines. As the mineral extraction in the area developed, the Shrewsbury and Chester Railway promoted a new line, the Wrexham and Minera Railway, which obtained the Royal Assent on 17 May 1861. It followed a longer, southerly course to gain height with gentler gradients, although they were still daunting. It ran from a junction south of Wrexham, at Croes Newydd, to Brymbo, where it joined the earlier branch line. It opened on 22 May 1862.
Traffic to and from Minera continued to use the earlier railway west of Brymbo. The Moss (western) incline on the original Minera line was not required, and it was closed. The eastern incline continued in use for the time being, serving Moss and Westminster collieries.[8][9]
The situation in 1865

The Mining Journal of 29 July 1865 summarised the railway situation at the time:
The only railway accommodation in this district at the moment is that afforded by the Great Western Railway... there is a steep incline (The Wheatsheaf Incline) averaging about 1 in 15 for about half a mile in length up which the empty trucks are drawn with a wire rope by the weight of the full trucks coming down. At the top of this incline there is a short tunnel which brings the line into the Moss Valley close by the Moss Pits of the Westminster Colliery. From this two branches go up the valley, one on the west side to Mr Clayton’s Bryn Mally Pits and another on the east side to Mr Clayton’s Pendwllyn Pits and to the Frood Pits and blast furnaces. From the Moss Valley to the Brymbo Valley the line was carried up the west side of the Moss Valley opposite the tunnel by a very steep incline (The Moss Valley Incline) of nearly 1 in 4 then through a tunnel about a quarter of a mile long which opened into the Brymbo Valley nearly opposite the Brymbo furnaces.
In the Brymbo Valley two branches were extended south, one on the east side of the Valley to the Nant Pits of the Westminster Company and to the pits of the Broughton Company and another on the west side of the Valley to the pits of the Vron Colliery. Northward the line is continued skirting the western side of the Brymbo Valley until it debouches into a branch valley of the Nantyffrith along which, skirting the outcrop of the measures, it continues its course tor about three miles to the Minera lime quarries and lead mining district.
As far as the Moss Valley (comprising the Moss pits of the Westminster Company and the Bryn Malley and Erood Pits) was concerned this arrangement gave sufficient accommodation. No practical difficulty was found in working any reasonable traffic over the Wheatsheaf Incline. With regard to the Brymbo Valley (including the Brymbo, Vron and Broughton Pits) the case was very different. The Moss Valley Incline was a serious stumbling block over which it was practically found that no considerable traffic could be worked. When the pressure came it was found impossible to time the full trucks so as to bring up the empties so that it more than once happened that the collieries were brought to a standstill in a time of flourishing trade for want of trucks which were lying at the bottom of the incline almost within sight of the pits where they were required. This was to some extent met by the erection of a stationary steam engine at the top of the Moss Valley Incline for the purpose of drawing up the empty trucks, an arrangement which was found to palliate but not to remedy the evil. About four years ago this was effected by the making of a branch line going directly up the Brymbo Valley starting from the main line about half a mile south of Wrexham and joining the branch already made to the Broughton Colliery along the east side of the Valley.

All the traffic from Minera and from the works in the Brymbo Valley is now worked over this branch, the Moss Valley Incline and tunnel being entirely disused; indeed at present there is no railway communication between the two valleys any traffic between them having to go round by Wrexham. This branch has been an immense boon to the entire district for not only has it given facilities to the collieries in the Brymbo valley and enable them to do a trade which before would have been impossible but it has also helped those in the Moss Valley by relieving the Wheatsheaf Incline over which the present traffic of the valley can be worked with ease and comfort.[10]
The Brynmally Colliery branch had a gradient of 1 in 30; it "ran along the street in Moss so that householders were obliged to cross the tracks to enter their doors".[11]
Wrexham, Mold and Connah's Quay Railway
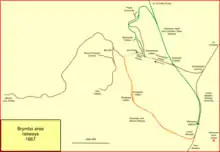
The continuing demand for mineral transport led to the promotion of the Wrexham, Mold and Connah's Quay Railway, authorised on 7 August 1862. It was built from Wrexham to join the Buckley Railway, a former horse tramway that had been upgraded, and together the two short lines gave access to a wharf on the River Dee, and to a connection with the Chester and Holyhead Railway. The line opened on 1 January 1866, for mineral traffic, and for passengers after improvements, on 1 May 1866.
There was a short spur to the Ffrwd Colliery, and a short spur to Brynmally. These were apparently the only WM&CQR branches in the Wrexham area at first.[12][13]
Wrexham and Minera Extension Railway
The LNWR (through the Chester and Holyhead Railway) had built a branch line from Mold to coal pits at Tryddyn (Treuddyn), near Coed Talon. The point of junction on the Mold main line was called Tryddyn Junction.
On 5 July 1865 the Wrexham and Minera Railway (which was of course a GWR satellite) obtained powers to extend from Brymbo to join the Tryddyn line. This would give the GWR access to Mold, then an important market town. For the purposes of the Act it was known as the Wrexham and Minera Extension Railway.
Wrexham and Minera Joint Railway
The LNWR wanted access to Brymbo and negotiation resulted in transfer of the powers (no construction work had yet been done on the railway) were transferred to the GWR and LNWR jointly by Act of 11 June 1866, and the proposed line became known as the Wrexham and Minera Joint Railway.[note 3]
Pits at Coed Talon and Ffrith were being developed at this time, and the LNWR decided that the earlier Tryddyn line was unsuitable. A new line was authorised from a new Ffrith Junction, near Padeswood on the Mold line, to Ffrith, making a junction with the Tryddyn line at Coed Talon.
The new LNWR line (from Ffrith Junction to Ffrith) was opened in 1870, and the original Tryddyn line was closed, although it was reopened later. The joint line on to Brymbo was not yet ready.[14][15]
As authorised, the Wrexham and Minera Joint Railway was to run from Brymbo to Coed Talon, but before opening it was altered. Train operation was to be joint; at one time trains were operated by the LNWR and GWR on alternate days. However the infrastructure was divided, the LNWR having sole responsibility on the Coed Talon side of a point 2m 67 ch from Brymbo, near Pantystain level crossing.[16]
A boundary stone is clearly marked on contemporary maps, and the Joint Line ran from Brymbo to the boundary stone.[17][18][19]
By an Act of 1871 the Wrexham & Minera Joint system was divided as between the GWR/LNWR jointly and the GWR alone; an end-on junction was determined at a point south of Coed Talon and north of Llanfynydd where mileposts were set up showing the distance to Paddington (to the south) and to Euston (to the north). The immediate mileage north of Brymbo (GW) became the responsibility of the GWR. At the divergence of the line from the W&M track proper, a large sandstone boundary stone was embedded; this read 'GWR' on the one side and 'L&NW & GW Joint Railway' on the other. Although the Act of 1871 made this stone inaccurate, it remains to this day (1990).[note 4][20]
Disparaging remarks about the line were made during hearings in 1881 for WM&CQR extensions:
There was general agreement about this Brymbo—Coed Talon link, it is practically a blocked line - 'it is of no use whatever, any more than if it did not exist’. … commercially, and as to our traders, it is not worth a rap'. Counsel for the WMCQR said it was a line straight out of PUNCH.[note 5] It was worked on alternate days by the GWR and LNWR: Tuesdays and Fridays were LNWR days and Mondays and Thursdays GWR days; the GWR engine starts from Brymbo and the LNWR one from Coed Talon or Mold, only one engine in steam being allowed on the line at a time. What becomes of the other two days I do not know.[21]
The line between Coed Talon and Brymbo, nearly three miles in length, opened to goods trains on 27 January 1872.[14] It continued to be known as "the Joint Line".
The Wrexham and Minera Railway joins the GWR
The original Wrexham and Minera Railway (from Wrexham to Brymbo, but inactive west of Moss) vested in the GWR in 1871.[14]
GWR: Moss Valley branch and Brymbo line improvements
The GWR built a Moss Valley branch of 3 miles, authorised on 21 July 1873, and opened in 1882;[note 6] it ran up to Ffrwd Ironworks from a junction with the W&MR main line half a mile west of Croes Newydd, through Gatewen, to join the original access from Wheatsheaf Junction and thus continue access to collieries further north - Brynmally and Ffrwd.
The inclined plane was retained, as it served other industrial sites. It was finally closed in October 1908.[note 7] Gwersyllt Colliery had a connection below the inclined plane and for the time being continued to be connected direct from Wheatsheaf Junction after 1908.[14][22][23]
The GWR Wrexham to Brymbo line was doubled, and opened to passengers on 24 April 1882.[24]
Gatewen branch built privately
The WM&CQR had been built in part because of dissatisfaction with facilities provided to coal owners and others by the monopoly GWR. Now that the WM&CQR main line had been built, there was increasingly bitter complaint from those not reached by the limited branch network of the Wrexham company. In 1881 the proprietors of the Gatewen Colliery decided to build a branch line themselves, from Stansty on the Wrexham line. The junction later became Brymbo North Junction. The line was built without Parliamentary authority, and opened on 8 or 17 June 1882.[22]
WM&CQR improvements
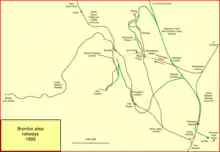
After a period of dormancy forced by lack of money, the Wrexham, Mold and Connah's Quay Railway obtained powers on 25 July 1882 to improve its main line. At the same time, it was disclosed that the Ffrwd and Brynmally branches were out of use due to lack of traffic.[25] Nevertheless, the 1882 Act authorised a new WM&CQR branch to Brymbo.This unwelcome incursion was hotly opposed in Parliament by the GWR.
The line as approved was from triangular junction near Gwersyllt to Brymbo; the northern arm of the triangular junction was the privately built Gatewen Colliery line, soon to be called Brymbo Junction. The line would connect Plas Power colliery (newly opened, and already served by the GWR line) and the Brymbo works, with a southward line from Brymbo to Vron, parallelling the GWR Vron branch. There would also be a southward extension from Brynmally to the Westminster Colliery. Gradients on these lines would be stiff.[26][27]
The Brymbo line opened to Moss & Pentre in 1882, and to Plas Power in June 1884, making a junction with the Wrexham and Minera line there. Completion to Brymbo followed in 1887, and the line opened to passengers on 1 August 1889.[28]
The line was very steeply graded, climbing all the way to Brymbo, with only short sections of double track. At first there were four trains daily between Wrexham and Brymbo, with two additional trains on Saturday. Notwithstanding the gradients, journey time was 23 minutes in each direction. By 1900 a remarkably frequent passenger service was operated between Wrexham and Brymbo.[29]
A further branch from Brymbo to Vron Colliery opened on 8 October 1888; this had steep gradients up to 1 in 27.[30][28]
A branch from the Ffrwd branch to Westminster Colliery opened on 27 April 1884.[31][32]
More passenger routes
On 2 May 1898 LNWR passenger trains started running from Mold to Brymbo, using the former joint line. There were four trains a day.[33] On the GWR line from Brymbo to Minera, passenger trains started operating as far as Coed Poeth on 15 November 1897, and the passenger service was extended to Berwig in 1905. From this time the motor-train system favoured by the GWR was used: a single coach incorporated a small steam engine; the arrangement was economical on lightly used passenger services, and a number of motor halts were opened to take advantage of the system. The Moss Valley branch received a similar passenger service from 1 May 1905, running from Wrexham as far up the valley as Moss Platform.[34]
WM&CQR absorbed
The WM&CQR had long been in financial difficulties, and acquisition by the Great Central Railway (formerly the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway) was authorised by Act of 22 July 1904; it became effective on 1 January 1905.[35]
Passenger train services
The 1910 Bradshaw's Guide shows thirteen trains each way between Wrexham and Brymbo, with most of them continuing to Berwig. There were several additional trains on Saturdays, but none at all on Sundays. All the trains were "Motor Cars: One Class Only". The term motor car referred to the self contained steam railway coach.
The Moss Valley line had ten trains each way, with several additional Saturday-only services.
The WM&CQR line, now shown as "Great Central", had eleven trains each way, also with several additional Saturday trains. The trains are described as "Motor Cars, with the exception of Saturdays after 2 aft.". In other words, loadings on Saturday afternoons were expected to be too heavy for the limited capacity of the railmotor vehicles. The route had the advantage of running to the Central station at Wrexham; the GWR Wrexham General station was not situated close to the town centre, but was less convenient for the housing area at Brymbo. This was one of the few areas where the Great Central Railway ran railmotors.[36]
There were four trains each way between Mold and Brymbo, on the LNWR and GWR joint line; there was an additional train on Wednesdays and Saturday.[37]
Later in the twentieth century
The WM&CQR passenger service was not consistently profitable, and during the manpower shortage of World War I, its passenger trains were withdrawn, on 1 March 1917.[38]
In 1923 the main line railways of Great Britain were "grouped" into one or other of four new large companies. The Great Central Railway, which now owned the WM&CQR network, was a constituent of the new London and North Eastern Railway. The Great Western Railway joined with other companies and formed the new Great Western Railway.
After 30 December 1930 passenger trains ceased to operate on the GWR Brymbo lines, as a result of road competition. Paradoxically the LNWR and GWR joint service from Mold continued for the time being, providing the only passenger connection to Brymbo, though by 1947 there were only 2 trains a day.[39] It closed later, on 27 March 1950. The line was severed in 1952, operating from Brymbo as a stub to Ffrith.
The GWR Moss Valley line lost its passenger service at the end of 1930, and when Brynmally Colliery closed in 1935 the branch was completely closed.[40]
In the 1960s all ordinary goods services in the area were terminated, leaving only a connection for mineral traffic to Brymbo steelworks. This used the WM&CQR line at the upper extremity (together with the extreme upper end of the GWR Vron branch), and a new connection to the former GWR line at Plas Power, from there running to Croes Newydd. This arrangement was in operation from 1954 until 1958, resuming in 1965 until final extinction in 1970.[38]
Rail traffic to the Minera lime works also finished, in 1971. There were eight unmanned crossings on the short branch at the time of closure.[41]
Christiansen adds:
After opencast mining began at Vron, a railhead was established at the site of Gatewen Colliery, linked first by the part relaying of the WM & CQ Brymbo branch, and later of the GWR Moss Valley branch from Brymbo North, ending about 50yd north of the former Brymbo branch underbridge. Part of the WM & CQ branch was then converted into a road and lorries began running under the Moss line to reach storage bunkers. Access to Croes Newydd ceased when the ex-GWR Brymbo branch closed in 1982, but the link reopened in 1983 when ICI began stockpiling coal from the Point of Ayr Colliery near Prestatyn, at Gatewen. That usage ended in 1991.[42]
The railway activity in the area has now ceased.[43]
Location list
Minera line (GWR)
- Berwig; opened 1 May 1905; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 2 April 1917; closed 1 January 1931;
- Vicarage Crossing; opened 1 May 1905; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 2 April 1917; closed 1 January 1931;
- Coed Poeth; opened 15 November 1897; closed 1 January 1931;
- Pentresaeson; opened 20 March 1905; closed 1 January 1931;
- Brymbo West Crossing; opened 20 March 1905; closed 1 January 1931;
 Brymbo West Crossing in 1962 looking towards Brymbo. A Down freight is headed by a 56XX 0-6-2T; beyond is Brymbo Steelworks
Brymbo West Crossing in 1962 looking towards Brymbo. A Down freight is headed by a 56XX 0-6-2T; beyond is Brymbo Steelworks - Brymbo; opened 24 May 1882; closed 27 March 1950; served from Mold after closure of the passenger service from Wrexham;
- The Lodge; opened 1 July 1906; closed 1 January 1931;
- Plas Power; opened February 1883; closed 1 January 1931;
- Moss Valley Junction;
- Croes Newydd Junctions;
- Wrexham; main line station.
Moss Valley passenger line
- Moss Platform; opened 1 May 1905; closed 1 January 1931;
- Gwersyllt Hill; opened 1 May 1906; closed 1 January 1931;
- Pentre Broughton; opened 1 May 1905; closed 1 January 1931;
- Moss Valley Junction; above.
WM&CQR passenger branch
- Brymbo; opened 1 August 1889; closed 1 March 1917.
- Plas Power; connection from and to GWR lines; opened 1 August 1889; closed 1 March 1917;
- New Broughton Road; opened 1 May 1905; closed 1 March 1917;
- Moss & Pentre; opened 1 August 1889; closed 1 March 1917;
- Highfield Road; opened 1 May 1905; closed 1 March 1917;
- Brymbo West Junction;
- Brymbo North Junction.
Joint line
Notes
- ↑ Some sources spell the place Ffrwyd, but that is a mistake.
- ↑ The reference to "railway" in the company's title refers to the extensive siding and internal network at Brymbo.
- ↑ It did not, of course, approach either Wrexham or Minera.
- ↑ This seems to be a mistake; it would fit other, less specific, sources if Boyd had said "'LNWR' on one side and 'LNW and GW Joint Railway' on the other." Boyd's work was consistently thorough and painstaking, and if this is a mistake, it is surprising.
- ↑ A humorous and satirical periodical.
- ↑ Baughan gives 11 May 1881 on page 56, but adds: "Some sources give 20 March 1882." Boyd gives 8 May 1881 on page 172. However, the Wrexham Advertiser 14 January 1882, reported that the line was then still uncompleted
- ↑ Boyd gives October 1907.
References
- ↑ Peter E Baughan, A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain: volume 11: North and Mid Wales, David St John Thomas Publisher, Nairn, 1991, ISBN 0 946537 59 3, pages 36 and 37
- 1 2 Baughan, pages 37 to 39
- ↑ J I C Boyd, The Wrexham, Mold and Connah's Quay Railway, Oakwood Press, Headington, 1991, ISBN 0 85361 417 2, pages 45 to 46
- ↑ Boyd, page 50
- ↑ Boyd, pages 47 and 48
- ↑ Boyd, page 49
- ↑ Baughan, page 50
- ↑ Baughan, page 51
- ↑ Boyd, pages 48 and 49
- ↑ Quoted in Boyd, pages 51 and 52
- ↑ Boyd, page 170
- ↑ Baughan, page 54
- ↑ Boyd, pages 106, 122, 133 and 134
- 1 2 3 4 Baughan, pages 55 and 56
- ↑ Mark Casson, The World's First Railway System: Enterprise, Competition, and Regulation on the Railway Network in Victorian Britain, Oxford University Press, 2009, ISBN 9780199213979, page 218
- 1 2 R A Cooke, Atlas of the Great Western Railway, Wild Swan Publications Limited, Didcot, 1997, ISBN 1 874103 38 0
- ↑ Cooke, page 92
- ↑ Quick, for example Ffrith station, page 127
- ↑ Railway Clearing House Junction Diagrams 1915, David & Charles Reprints, Newton Abbot, 1969, ISBN 0 7153 4347 5, page 119
- ↑ Boyd, pages 153 and 154
- ↑ Evidence and argument in the House of Lords Committee for the 1881 WMCQR (Extensions and Dock) Bill, quoted in Boyd, page 175
- 1 2 Boyd, pages 171, 172 and 179
- ↑ Rex Christiansen, Forgotten Railways: North and Mid Wales, David St John Thomas, Newton Abbot, 1984, ISBN 978-0946537051, page 21
- ↑ Wrexham Advertiser 29 April 1882
- ↑ Boyd, page 182
- ↑ Boyd, page 177
- ↑ Boyd, page 182 onwards
- 1 2 Baughan, page 58
- ↑ Boyd, pages 271 to 288
- ↑ Boyd, pages 266 and 268
- ↑ Boyd, page 184
- ↑ Boyd, page 264
- ↑ Baughan, page 60
- ↑ Baughan, pages 60 and 61
- ↑ Boyd, page 231
- ↑ Christiansen, page 23
- ↑ Bradshaw's April 1910 Railway Guide, David and Charles, Newton Abbot, 1968, ISBN 0 7153 4246 0
- 1 2 Baughan, page 62
- ↑ "LMS timetable 102". timetableworld.com. June 1947. Retrieved 17 February 2022.
- ↑ Boyd, page 179
- ↑ Christiansen, page 21
- ↑ Christiansen, page 24
- 1 2 Col M H Cobb, The Railways of Great Britain: A Historical Atlas, Ian Allan, Shepperton, 2003, ISBN 978-0711030022
- ↑ Michael Quick; Railway Passenger Stations in England, Scotland and Wales: A Chronology, Railway and Canal Historical Society, Richmond, 2002