Bussigny-sur-Oron | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Bussigny-sur-Oron | |
 Bussigny-sur-Oron  Bussigny-sur-Oron | |
| Coordinates: 46°34′N 06°51′E / 46.567°N 6.850°E | |
| Country | Switzerland |
| Canton | Vaud |
| District | Lavaux-Oron |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Raymond Casellini |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1.17 km2 (0.45 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 769 m (2,523 ft) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 77 |
| • Density | 66/km2 (170/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Les Cabris |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (Central European Time) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (Central European Summer Time) |
| Postal code(s) | 1607 |
| SFOS number | 5781 |
| Surrounded by | Saint-Martin (FR), Maracon, Ecoteaux, Chesalles-sur-Oron |
| Website | Profile (in French), SFSO statistics |
Bussigny-sur-Oron is a former municipality in the district of Lavaux-Oron of the Canton of Vaud, Switzerland. The municipalities of Bussigny-sur-Oron, Châtillens, Chesalles-sur-Oron, Ecoteaux, Oron-la-Ville, Oron-le-Châtel, Palézieux, Les Tavernes, Les Thioleyres and Vuibroye merged on 1 January 2012 into the new municipality of Oron.[1]
History
Bussigny-sur-Oron is first mentioned in 1433 as Bussignye. In 1517 it was mentioned in a land registry of Count Jean II de Gruyère.[2]
Geography
Bussigny-sur-Oron has an area, as of 2009, of 1.2 square kilometers (0.46 sq mi). Of this area, 0.92 km2 (0.36 sq mi) or 79.3% is used for agricultural purposes, while 0.16 km2 (0.062 sq mi) or 13.8% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 0.1 km2 (25 acres) or 8.6% is settled (buildings or roads).[3]
Of the built up area, housing and buildings made up 3.4% and transportation infrastructure made up 4.3%. Out of the forested land, all of the forested land area is covered with heavy forests. Of the agricultural land, 30.2% is used for growing crops and 47.4% is pastures, while 1.7% is used for orchards or vine crops.[3]
The municipality was part of the Oron District until it was dissolved on 31 August 2006, and Bussigny-sur-Oron became part of the new district of Lavaux-Oron.[4]
The small municipality is located near the Lausanne-Bulle road along the Mionnaz river.
The municipalities of Bussigny-sur-Oron, Châtillens, Chesalles-sur-Oron, Ecoteaux, Oron-la-Ville, Oron-le-Châtel, Palézieux, Les Tavernes, Les Thioleyres and Vuibroye are seeking approval from the Canton to merge on 1 January 2012 into the new municipality of Oron.[1]
Coat of arms
The blazon of the municipal coat of arms is Per pale, 1. Azure, two mullets of five above a crescent upward Or; 2. Or, a kid rampant Sable, langued Gules, horned and lined Argent.[5]
Demographics
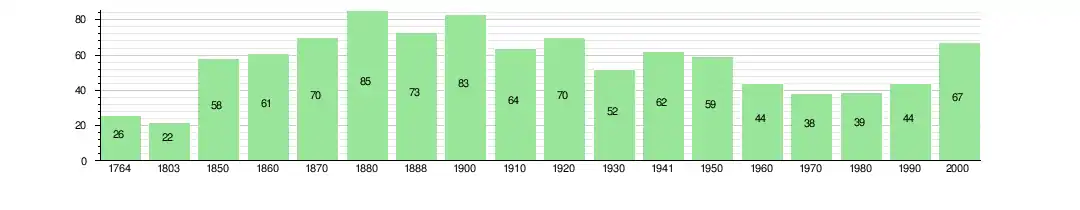
Bussigny-sur-Oron has a population (as of 2010) of 77. As of 2008, 6.8% of the population are resident foreign nationals.[6] Over the last 10 years (1999–2009 ) the population has changed at a rate of 25.4%. It has changed at a rate of 20.6% due to migration and at a rate of 1.6% due to births and deaths.[7]
Most of the population (as of 2000) speaks French (60 or 89.6%), with German being second most common (5 or 7.5%) and English being third (1 or 1.5%).[8]
The age distribution, as of 2009, in Bussigny-sur-Oron is; 7 children or 8.9% of the population are between 0 and 9 years old and 11 teenagers or 13.9% are between 10 and 19. Of the adult population, 13 people or 16.5% of the population are between 20 and 29 years old. 10 people or 12.7% are between 30 and 39, 14 people or 17.7% are between 40 and 49, and 7 people or 8.9% are between 50 and 59. The senior population distribution is 9 people or 11.4% of the population are between 60 and 69 years old, 6 people or 7.6% are between 70 and 79, there are 2 people or 2.5% who are between 80 and 89.[9]
As of 2000, there were 27 people who were single and never married in the municipality. There were 33 married individuals, 4 widows or widowers and 3 individuals who are divorced.[8]
As of 2000 the average number of residents per living room was 0.54 which is fewer people per room than the cantonal average of 0.61 per room.[7] In this case, a room is defined as space of a housing unit of at least 4 m² (43 sq ft) as normal bedrooms, dining rooms, living rooms, kitchens and habitable cellars and attics.[10] About 75% of the total households were owner occupied, or in other words did not pay rent (though they may have a mortgage or a rent-to-own agreement).[11]
As of 2000, there were 24 private households in the municipality, and an average of 2.7 persons per household.[7] There were 7 households that consist of only one person and 4 households with five or more people. Out of a total of 25 households that answered this question, 28.0% were households made up of just one person and there was 1 adult who lived with their parents. Of the rest of the households, there are 4 married couples without children, 10 married couples with children and 2 single parents with a child or children.[8]
In 2000 there were 12 single family homes (or 60.0% of the total) out of a total of 20 inhabited buildings. There were multi-family buildings (0.0%), along with 7 multi-purpose buildings that were mostly used for housing (35.0%) and 1 other use buildings (commercial or industrial) that also had some housing (5.0%).[12]
In 2000, a total of 24 apartments (96.0% of the total) were permanently occupied and one apartment was empty.[12] As of 2009, the construction rate of new housing units was 0 new units per 1000 residents.[7] The vacancy rate for the municipality, in 2010, was 0%.[7]
The historical population is given in the following chart:[2][13]
Politics
In the 2007 federal election the most popular party was the SVP which received 28.03% of the vote. The next three most popular parties were the Green Party (25.25%), the EDU Party (13.64%) and the SP (11.11%). In the federal election, a total of 22 votes were cast, and the voter turnout was 44.9%.[14]
Economy
As of 2010, Bussigny-sur-Oron had an unemployment rate of 3.9%. As of 2008, there were 10 people employed in the primary economic sector and about 3 businesses involved in this sector. No one was employed in the secondary sector or the tertiary sector.[7] There were 40 residents of the municipality who were employed in some capacity, of which females made up 37.5% of the workforce.
In 2008 the total number of full-time equivalent jobs was 8, all of which were in agriculture.[15]
In 2000, there were 11 workers who commuted into the municipality and 28 workers who commuted away. The municipality is a net exporter of workers, with about 2.5 workers leaving the municipality for every one entering.[16] Of the working population, 25% used public transportation to get to work, and 42.5% used a private car.[7]
Religion
From the 2000 census, 19 or 28.4% were Roman Catholic, while 26 or 38.8% belonged to the Swiss Reformed Church. Of the rest of the population, there were 8 individuals (or about 11.94% of the population) who belonged to another Christian church. There was 1 individual who was Islamic. 17 (or about 25.37% of the population) belonged to no church, are agnostic or atheist.[8]
Education
In Bussigny-sur-Oron about 21 or (31.3%) of the population have completed non-mandatory upper secondary education, and 12 or (17.9%) have completed additional higher education (either University or a Fachhochschule). Of the 12 who completed tertiary schooling, 58.3% were Swiss men, 33.3% were Swiss women.[8]
In the 2009/2010 school year there were a total of 9 students in the Bussigny-sur-Oron school district. In the Vaud cantonal school system, two years of non-obligatory pre-school are provided by the political districts.[17] During the school year, the political district provided pre-school care for a total of 665 children of which 232 children (34.9%) received subsidized pre-school care. The canton's primary school program requires students to attend for four years. There were 5 students in the municipal primary school program. The obligatory lower secondary school program lasts for six years and there were 4 students in those schools.[18]
As of 2000, there was one student in Bussigny-sur-Oron who came from another municipality, while 12 residents attended schools outside the municipality.[16]
References
- 1 2 Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz published by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office (in German) accessed 21 December 2011
- 1 2 Bussigny-sur-Oron in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- 1 2 Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics 2009 data (in German) accessed 25 March 2010
- ↑ Nomenklaturen – Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz Archived 2015-11-13 at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 4 April 2011
- ↑ Flags of the World.com accessed 08-August-2011
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office - Superweb database - Gemeinde Statistics 1981-2008 Archived June 28, 2010, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 19 June 2010
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Swiss Federal Statistical Office Archived November 16, 2011, at the Wayback Machine accessed 08-August-2011
- 1 2 3 4 5 STAT-TAB Datenwürfel für Thema 40.3 - 2000 Archived August 9, 2013, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 2 February 2011
- ↑ Canton of Vaud Statistical Office Archived 2015-03-16 at the Wayback Machine (in French) accessed 29 April 2011
- ↑ Eurostat. "Housing (SA1)". Urban Audit Glossary (PDF). 2007. p. 18. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 November 2009. Retrieved 12 February 2010.
- ↑ Urban Audit Glossary pg 17
- 1 2 Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB - Datenwürfel für Thema 09.2 - Gebäude und Wohnungen Archived September 7, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 28 January 2011
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB Bevölkerungsentwicklung nach Region, 1850-2000 Archived September 30, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 29 January 2011
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office, Nationalratswahlen 2007: Stärke der Parteien und Wahlbeteiligung, nach Gemeinden/Bezirk/Canton Archived May 14, 2015, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 28 May 2010
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB Betriebszählung: Arbeitsstätten nach Gemeinde und NOGA 2008 (Abschnitte), Sektoren 1-3 Archived December 25, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 28 January 2011
- 1 2 Swiss Federal Statistical Office - Statweb (in German) accessed 24 June 2010
- ↑ Organigramme de l'école vaudoise, année scolaire 2009-2010 Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine (in French) accessed 2 May 2011
- ↑ Canton of Vaud Statistical Office - Scol. obligatoire/filières de transition Archived 2016-04-25 at the Wayback Machine (in French) accessed 2 May 2011