| CCDC113 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | CCDC113, HSPC065, coiled-coil domain containing 113 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 616070 MGI: 3606076 HomoloGene: 40927 GeneCards: CCDC113 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 113 also known as HSPC065, GC16Pof6842 and GC16P044152, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCDC113 gene. The human CCDC113 gene is located on chromosome 16q21 and encodes 5,304 base pairs of mRNA and 377 amino acids.[5][6][7]
Gene
CCDC113 is located on chromosome 16q21 and encodes two distinct isoforms with isoform 2 containing one less alternate in-frame exon compared to the full length protein, isoform 1. Isoform 1 is composed of 5304 base pairs of mRNA which form the 9 exons that make up the coding sequence.[8]
.png.webp)
CCDC113, located between nucleotides 58283840 and 58317740 on chromosome 16, is surrounded between antisense genes PRSS54 and CSNK2A2 and downstream from GINS3 and NDRG4 on the sense strand. PRSS54 is a trypsin-like serine protease which codes for the inactive serine protease 54 precursor.[10] CSNK2A2 the casein kinase 2, alpha prime polypeptide contains a protein kinase domain and a catalytic domain.[11] GINS3 is essential for the initiation of DNA replication and replisome progression in eukaryotes.[12] NDRG4 a member of the N-myc downregulated gene family belonging to the alpha/beta hydrolase superfamily which encodes a cytoplasmic protein responsible for cell cycle progression and survival in primary astrocytes and may be involved in regulation of mitogenic signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells.[13]
Homology
Paralogs
CCDC113 has one known paralog CCDC96 which has a query cover of 27% and a max identity value of 34%.[14]
| Name | Species | Species Common Name | NCBI Accession Number | Length | Protein Identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCDC113 | Homo sapiens | Human | NP_054876.2 | 377aa | 100% |
| CCDC96 | Homo sapiens | Human | NP_699207.1 | 555aa | 34% |
Homologs
CCDC113 is highly conserved in all mammals and in organisms diverging back to Zebrafish, Danio rerio.[14]
| Species | Species common name | NCBI Accession Number (mRNA/Protein) | Length (bp/aa) | Protein Identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | Human | NM_014157.3 / NP_054876.2 | 5304bp/377aa | 100% |
| Pan troglodytes | Chimpanzee | XM_523504.4/ / XP_523504.2 | 5269bp/377aa | 99% |
| Mus musculus | Mouse | NM_172914.2 / NP_766502.1 | 1271bp/377aa | 78% |
| Felis catus | Cat | XM_003998086.1 / 410983617 | 1252bp/323aa | 69% |
| Xenopus (Silurona) tropicalis | Western Clawed Frog | XM_002931657.1 / 301604136 | 1395bp/441aa | 43% |
| Danio rerio | Zebrafish | NM_001006061.1 / NP_001006061.1 | 1154bp/358aa | 38% |
Protein
The CCDC113 protein is composed of 377 amino acids which form a secondary structure composed primarily of alpha-helices.[8][15] This protein contains a domain of unknown function DUF4201. There are many predicted post-translational modifications including phosphorylation, N-terminal acetylation, sumoylation, and N-glycosylation.[16]
Function
The function of CCDC113 is currently unknown.
Expression
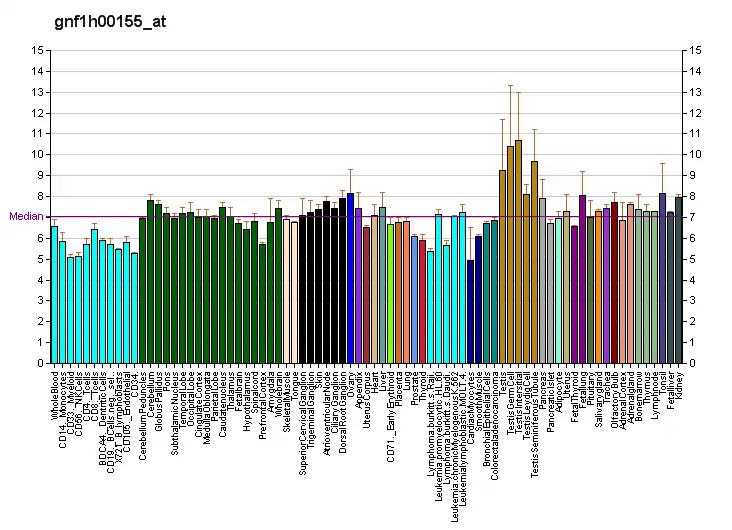
CCDC 113 is expressed at low levels in nearly all tissues of the body by RNA-seq including blood, lymph node, brain, heart, skeletal muscle, kidney, liver, colon, lung, thyroid, prostate, ovary, breast, adrenal gland, and adipocyte. The gene is also expressed in embryonic tissues and stem cells.[17] There are high levels of expression in the cerebellum and in the testis and surrounding tissues.[18]
Interactions
Regulatory elements of CCDC113 include transcription factors ATF2, FOXD1, LCR-F1, C/EBPalpha, Max, AREB6, CBF-A, CBF(2), c-Myc, and HIF.[8]
Interacting proteins found using two-hybrid screening techniques include GIT1; a G protein-coupled receptor kinase interacting ArfGAP, the cytoplasmic protein HAP1; Huntingtin-associated protein 1,[19] IMMT, an inner mitochondrial membrane protein, and PFN2; Profilin 2- ubiquitous actin monomer binding protein.[8]
Clinical significance
Studies have linked expression of CCDC113 in cancerous tissues to mutations present in the coding sequence. Missense mutations at location 86 from Arginine to Tryptophan (R86Y) and at R180C are related to adenocarcinomas of the colon. Two point mutations have also been linked to adenocarcinomas of the rectum, a missense mutation of R361Q and a base pair point mutation c972t. Serous carcinoma of the ovaries has been related to a missense mutation S6F.[20]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000103021 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000036598 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, Gassenhuber J, Glassl S, Ansorge W, Bocher M, Blocker H, Bauersachs S, Blum H, Lauber J, Dusterhoft A, Beyer A, Kohrer K, Strack N, Mewes HW, Ottenwalder B, Obermaier B, Tampe J, Heubner D, Wambutt R, Korn B, Klein M, Poustka A (Mar 2001). "Toward a catalog of human genes and proteins: sequencing and analysis of 500 novel complete protein coding human cDNAs". Genome Res. 11 (3): 422–35. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072. PMID 11230166.
- ↑ Zhang QH, Ye M, Wu XY, Ren SX, Zhao M, Zhao CJ, Fu G, Shen Y, Fan HY, Lu G, Zhong M, Xu XR, Han ZG, Zhang JW, Tao J, Huang QH, Zhou J, Hu GX, Gu J, Chen SJ, Chen Z (Nov 2000). "Cloning and functional analysis of cDNAs with open reading frames for 300 previously undefined genes expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells". Genome Res. 10 (10): 1546–60. doi:10.1101/gr.140200. PMC 310934. PMID 11042152.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: CCDC113 coiled-coil domain containing 113".
- 1 2 3 4 "Coiled-Coil Domain Containing 113". GeneCards. Retrieved May 8, 2013.
- "CCDC113 coiled-coil domain containing 113 Homo sapiens (human)". NCBI. Retrieved May 8, 2013.
- ↑ "Inactive Serine Protease 54 Precursor (Homo sapiens)". NCBI. Retrieved May 8, 2013.
- ↑ "CSNK2A2 casein kinase 2, alpha prime polypeptide [ Homo sapiens (human) ]". NCBI. Retrieved May 8, 2013.
- ↑ "GINS3 GINS complex subunit 3 (psf3 homolog)". NCBI. Retrieved May 8, 2013.
- ↑ "NDRD4 NDRG family member 4". NCBI. Retrieved May 8, 2013.
- 1 2 "Basic Local Alignment Search Tool". BLAST. NCBI. Retrieved May 8, 2013.
- ↑ Kelley LA, Sternberg MJ (2009). "Protein structure prediction on the Web: a case study using the Phyre server". Nat Protoc. 4 (3): 363–71. doi:10.1038/nprot.2009.2. hdl:10044/1/18157. PMID 19247286. S2CID 12497300.
- ↑ "Bioinformatics Resource Portal". ExPASy. Retrieved May 8, 2013.
- ↑ "CCDC113 (coiled-coil domain containing 113)". BioGPS. Retrieved 2013-04-22.
- 1 2 Su AI, Wiltshire T, Batalov S, Lapp H, Ching KA, Block D, Zhang J, Soden R, Hayakawa M, Kreiman G, Cooke MP, Walker JR, Hogenesch JB (April 2004). "A gene atlas of the mouse and human protein-encoding transcriptomes". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (16): 6062–7. Bibcode:2004PNAS..101.6062S. doi:10.1073/pnas.0400782101. PMC 395923. PMID 15075390.
- ↑ Gutekunst CA, Li SH, Yi H, Ferrante RJ, Li XJ, Hersch SM (October 1998). "The cellular and subcellular localization of huntingtin-associated protein 1 (HAP1): comparison with huntingtin in rat and human". J. Neurosci. 18 (19): 7674–86. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-19-07674.1998. PMC 6793025. PMID 9742138.
- ↑ "El Dorado". El Dorado. Retrieved 2013-04-25.
External links
- Human CCDC113 genome location and CCDC113 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.