 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
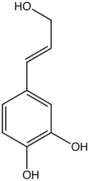
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-[(1E)-3-Hydroxyprop-1-en-1-yl]benzene-1,2-diol | |
| Other names
Caffeyl alcohol, Caffeoyl alcohol, 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamyl alcohol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O3 | |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 144 to 145 °C (291 to 293 °F; 417 to 418 K) |
| moderate | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Caffeyl alcohol is the organic compound with the formula (HO)2C6H3-4-CHCHCH2OH. This colourless solid is related to catechol by attachment to allyl alcohol. It is the precursor to one of the three principal lignols.
Preparation and occurrence
In the laboratory, caffeyl alcohol can be synthesized from 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde.[1] It is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of coniferyl alcohol, the conversion being effected by caffeate O-methyltransferase.[2]
Related compounds
Two related compounds are caffeyl aldehyde and caffeic acid, the latter also being a minor component of coffee.[3]
References
- ↑ Karl Herrmann “Caffeyl Alcohol” Pharmazie 1953, volume 8, 303.
- ↑ John M Humphreys, Clint Chapple “Rewriting the Lignin Roadmap” Current Opinion in Plant Biology 2002, volume 5, 224–229. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(02)00257-1
- ↑ Rinantonio Viani, Marino Petracco “Coffee” in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry” Wiley-VCH, 2007, Weinheim.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.