
A camelback locomotive (also known as a Mother Hubbard or a center-cab locomotive) is a type of steam locomotive with the driving cab placed in the middle, astride the boiler. Camelbacks were fitted with wide fireboxes which would have severely restricted driver visibility from the normal cab location at the rear.
Development
The camel and the camelback design were developed separately by two different railroads in different eras. Though the name is often incorrectly used interchangeably, they had little in common other than the placement of the cab. Unlike the later Camelbacks, Camels had cabs that rode atop the boiler. Ross Winans wanted to put as much weight on the driving wheels as possible to increase traction. Camelbacks have a cab that straddles the boiler. While Camelbacks have the same idea of moving the cab forward, they had it for different reasons. Camelbacks were developed to allow for the use of larger fireboxes, such as the Wootten, which would obstruct the engineer's view from a conventionally placed cab. Camelbacks were particularly known for being used on the Central Railroad of New Jersey and the Reading Railroad.
Early use

The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad began to look into developing high-powered steam locomotives in the early 1840s, and in 1844–1847 built a series of locomotives nicknamed "muddiggers". As with many early B&O locomotives, a spur gear drive was used to connect the main shaft to the driving wheels. The long 0-8-0 wheelbase pushed this connection to the back of the locomotive and caused the floor of the cab to be lifted up above the whole assembly.

In 1853 Ross Winans, who had designed the "muddiggers", built the first of a series of 0-8-0 camel locomotives. These had long cabs that ran from the back of the smokebox to the front of the firebox. The firebox itself sloped back on the earliest models. The fireman worked from a large platform on the tender, and in some cases had a chute to allow him to deliver coal to the front of the grate.
Also in 1853, Samuel Hayes, the Master of Machinery for the railroad, had built a series of camel 4-6-0 locomotives for passenger service. The layout of the locomotive was roughly the same as for Winans' freight locomotives, except for the addition of the four-wheel leading bogie. Copies and variations on these locomotives were built into the 1870s, with the last retirements coming in the 1890s. These were called the "Hayes Ten-Wheelers". Many camelback locomotives used anthracite. The B&O examples burned conventional bituminous coal. The large fireboxes of these locomotives were made obsolete by better boiler design.
The B&O Railroad Museum has recently restored their Camel Locomotive and returned it to display. It now is in its original colors and markings for the first time since it left the Mt. Clare Shops in 1869. The Museum also has a Central of New Jersey Camelback, the No. 592, which was donated to the Museum in the 1950s.
The Wootten firebox
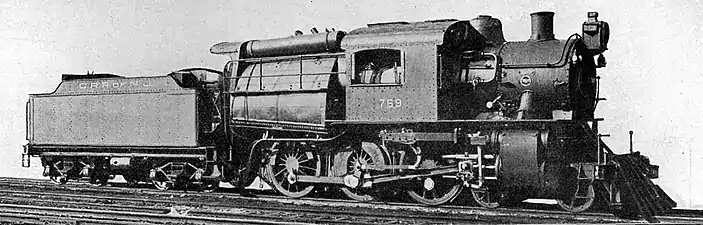
John E. Wootten developed the Wootten firebox to effectively burn culm, anthracite waste, which was a plentiful, cheap source of fuel. Wootten determined that a large, wide firebox would work best. As the successful trailing truck used to support large fireboxes had not yet been developed, Wootten instead mounted his huge firebox above the locomotive's driving wheels.
First Camelbacks
Originally Wooten firebox engines were built with the cab sitting upon the top of the firebox, in the rear. The first Wooten firebox locomotives 4-6-0 "Ten Wheeler" types were built in early 1877 by the P&R's Reading, Pennsylvania shops. However they were not a "camelback" design. The Wooten firebox proved a success; the fuel cost saving was about $2,000 a year (approx. $30,000 now). A Wooten firebox engine, P&R 412 was exhibited at the 1879 International Technological Exhibition in Paris, where it won a silver medal. Following the exhibition it toured Europe, first to sell anthracite coal and later to sell Wooten firebox engines. The engine could not demonstrate on European lines because, due to the cab sitting on top of the firebox, it was too tall to fit under bridges and through tunnels. The 412's engineer C. Gilbert Steffe came up with a solution. In a French railroad yard, he had the cab removed from the firebox and placed forward of the firebox on the running boards, creating the first camelback locomotive. The engine demonstrated in France and Italy through 1879 and was returned to the U.S. in 1880. Because the camelback design allowed for a taller firebox, the design was used by many of the railroads operating in the anthracite regions of Pennsylvania. By the time of World War 1, the diameter of locomotive boilers had increased to the point the cab astride the boiler was no longer practical and railroads stopped building camelbacks and subsequent Wooten firebox engines were built with conventional end cabs. Camelback engines were constructed with many different wheel arrangements, 0-4-0, 0-6-0, 0-8-0, 2-6-0, 2-8-0, 2-8-2, 4-4-0, 4-4-2, and 4-6-0 were the most common wheel arrangements. The largest ones had a 0-8-8-0 arrangement and were the only articulated Camelbacks built.
Later Camelbacks
By the 1920s, many Camelback Ten Wheelers with boiler pressure at 200psi were in daily use pulling passenger trains on the Lehigh Valley, the Philadelphia and Reading, and the Central Railroad of New Jersey, particularly the last two. For their relatively small size, they were powerful, quick to accelerate, very stable at speed, and could be operated as fast as 90 miles per hour such as on the Reading's Atlantic City line. Some continued in service into the 1950s.[1]
Safety concerns

The Camelback's cab astride the boiler design raised concerns for its crew. The separation of engineer and fireman limited their ability to communicate with each other. Also, the engineer was perched above the side-rods of the locomotive, vulnerable to swinging and flying metal if anything rotating below should break; in many cases, the fireman was exposed to the elements at the rear.
The Philadelphia and Reading's crews referred to these locomotives as Mother Hubbards. The B&O crews, who had co-use of the Reading's line from Philadelphia to Bound Brook NJ (the Reading's junction with the Central RR of New Jersey's line to Jersey City across from New York City) called the Camelbacks "Snappers" in reference to a possible side rod snapping and flailing into the cab.[2] Many Camelbacks were converted into end-cab locomotives. The advent of the mechanical stoker which moved coal from the tender to the locomotive and its associated underfloor machinery placed cab floors and tender decks higher, and from that vantage point the engineer was safe.
Survivors
There are five known Camelback locomotives to survive today:
- Central Railroad of New Jersey 4-4-2 No. 592, at the Baltimore & Ohio Railroad Museum in Baltimore, Maryland.[3]
- Baltimore & Ohio Railroad 4-6-0 No. 173, at the National Museum of Transportation, St. Louis.
- Baltimore & Ohio Railroad 4-6-0 No. 305 (formerly No. 217), at the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad Museum in Baltimore, Maryland.
- Delaware, Lackawanna & Western 4-4-0 No. 952, at the Museum of Transportation in St. Louis, Missouri.
- Reading Company 0-4-0 No. 1187, at the Age of Steam Roundhouse Museum in Sugarcreek, Ohio. (awaiting cosmetic restoration)
Owning railroads
- Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway
- Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
- Canadian Pacific Railway
- Central Railroad of New Jersey
- Chicago and Eastern Illinois Railroad
- Chicago and Indiana Coal Railroad
- Choctaw, Oklahoma and Gulf Railroad
- Delaware and Hudson Railway
- Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad
- Bath & Hammondsport Railroad
- Erie Railroad
- Hecla and Torch Lake Railroad
- Huntingdon & Broad Top Mountain Railroad
- Lehigh and Hudson River Railway
- Lehigh and New England Railroad
- Lehigh Valley Railroad
- Long Island Rail Road
- Maine Central Railroad
- Missouri-Kansas-Texas Railroad
- Nashville, Chattanooga and St. Louis Railway
- New York, Ontario and Western Railway
- New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway
- Pennsylvania Railroad
- Reading Railroad
- St. Clair Tunnel Company
- Staten Island Rapid Transit
- Southern Pacific Railroad
- Union Pacific Railroad
- Wheeling and Lake Erie Railroad
References
- ↑ Baltimore and Ohio Museum Website information
- ↑ Baltimore and Ohio Museum discussion of their Camelback display locomotive
- ↑ "CNJ No. 592". B&O Railroad Museum. Archived from the original on December 29, 2018. Retrieved March 25, 2019.
- Barris, Wes. "Camelback Locomotives". Archived from the original on 2004-12-07. Retrieved December 10, 2004.
- Sagle, Lawrence W. (1964). B&O Power: Steam, Diesel and Electric Power of the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad 1829–1964. Alvin F. Staufer.
- Ames, Gregory P. (2018). "Mother Hubbard's Bone of Contention: In Search of the ICC "Ban" on Mother Hubbard Locomotives". Railroad History No.219.
- Reed, Brian (1971). Camels and Camelbacks, Locomotives in Profile, vol. 1. Doubleday.
- Holton, James (1989). The Reading Railroad: History of a Coal Age Empire, vol. 1. Garrigues House.