 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
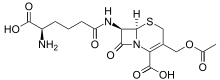
| IUPAC name
3-[(Acetyloxy)methyl]-7β-(N6-L-homoglutamino)-3,4-didehydrocepham-4-carboxylic acid | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(6R,7R)-3-[(Acetyloxy)methyl]-7-[(5R)-5-amino-5-carboxypentanamido]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
7-(5-Amino-5-carboxyvaleramido)cephalosporanic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.456 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H21N3O8S | |
| Molar mass | 415.42 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Cephalosporin C is an antibiotic of the cephalosporin class. It was isolated from a fungus of the genus Acremonium and first characterized in 1961.[1] Although not a very active antibiotic itself, synthetic analogs of cephalosporin C, such as cefalotin, became some of the first marketed cephalosporin antibiotic drugs.
Cephalosporin C strongly absorbs ultraviolet light, is stable to acid, is non-toxic and has in vivo activity in mice.[2] Cephalosporin C, which has a similar structure to penicillin N, was never commercialized.
Cephalosporin C was a lead compound for the discovery and production of many other cephalosporins.[2] Cephalosporins are drugs used for some people who are allergic to penicillin.
Uses
Cephalosporins are used to treat bacterial infections such as respiratory tract infections, skin infections and urinary tract infections. When a cephalosporin or any other antibiotic is given as a treatment, the medication should be taken for the fully prescribed time even if symptoms disappear.[3]
Mechanism of action
Cephalosporin C acts by inhibiting penicillin binding proteins.
Side effects
These are allergic reactions to the drug and require medical attention:[3]
- itching
- swelling
- dizziness
- rash
- trouble breathing
- vomiting
- severe stomach cramps
- bloody diarrhea
- fever
- weakness
- fast heartbeat
Chemistry
Cephalosporin C has weak activity to the staphylococci infection, which was 0.1% activity. This decrease in activity was due to the replacement of the D-α-aminoadipic acid side chain with phenylacetic acid.[2]
Biochemistry
Cephalosporin C is the product of the biosynthesis pathway of third generation cephalosporins. This is done by exchanging the acetyl CoA into DAC.[4]
To achieve cephalosporin C as the end product, there are 6 genes reported to be in control of the pathway.[4]
References
- ↑ Abraham, E. P.; Newton, G. G. F. (1961). "Structure of cephalosporin C". Biochemical Journal. 79 (2): 377–393. doi:10.1042/bj0790377. PMC 1205850. PMID 13681080.
- 1 2 3 Kardos, Nelson; Demain, Arnold L. (November 2011). "Penicillin: the medicine with the greatest impact on therapeutic outcomes". Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 92 (4): 677–687. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3587-6. ISSN 0175-7598. PMID 21964640. S2CID 39223087.
- 1 2 "CEPHALOSPORINS - INJECTION side effects, medical uses, and drug interactions". MedicineNet. Retrieved 2019-05-06.
- 1 2 Singh, Khusbu; Mohapatra, Pradumna K.; Pati, Sanghamitra; Dwivedi, Gaurav Raj (2019). "Genetics and Molecular Biology of Genes Encoding Cephalosporin Biosynthesis in Microbes". New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering. pp. 25–34. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-63503-7.00002-4. ISBN 9780444635037. S2CID 91263634.