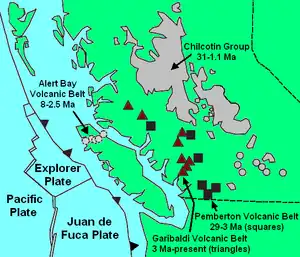
The Chilcotin Group, also called the Chilcotin Plateau Basalts, is a large area of basaltic lava that forms a volcanic plateau running parallel with the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt in south-central British Columbia, Canada.
Predominantly, during Miocene and Pliocene times, a medium-sized volcanic field of overlapping vents occurred in British Columbia's Interior Plateau. The distribution is assumed to engulf up to 50,000 km2 of the Pacific Northwest, forming a medium-sized large igneous province, of volume 3300 km3.[1] Volcanism occurred as late as Oligocene time, but continues sporadically up to present. Eruptions were most vigorous 6-10 million years ago and 2-3 million years ago, when most of the basalt was released. Less extensive eruptions continued 0.01 to 1.6 million years ago.[2]
These lava flows have been dominantly exposed by erosion resulting from the great floods that flowed in this region throughout the past ice ages, which laid bare many layers of the basalt flows along the Fraser Canyon from Soda Creek south to Canoe Creek elsewhere along the Chilcotin, Chilko, Chilanko and Taseko Rivers, and also to the east of the Fraser River at Chasm Provincial Park and along the Upper Deadman River. Prior to Late Pleistocene glacial erosion these centers formed a series of coalesced, low-profile shield volcanoes of unknown volume and distribution.
The Chilcotin Group were thought to potentially be linked to the partly coeval Columbia River Basalt Group. However, its morphology and geochemistry have been proven much similar to other volcanic plateaus such as the Snake River Plain in Idaho and parts of Iceland (Bevier, 1983).
Formation of the Chilcotin Plateau Basalts

The distribution and volume of the Chilcotin Group is unknown due to extensive Pleistocene glacial cover. This presumably glacial "drift" is very thick, and in most regions completely obscures the volcanism. Individual vents for basalt volcanism include small cinder cones, volcanic plugs, and gabbroic feeders, which locally crosscut lava flows. Recent studies indicate that the volume of the Chilcotin Group is much less than previously thought, and that the "Plateau" is likely Eocene in age. This means that the Chilcotin is likely composed of many local volcanic vents, that were of small volumes that fed into the paleo-landscape, and subsequently are found in the major river systems that we see at present.
Prior to 16 million years ago, the western Cascade Volcanic Arc stratovolcanoes erupted with periodic regularity for over 27 million years, even as they do today. The ultimate cause of this volcanism is still up for debate, however, the most widely accepted idea is that a back-arc basin behind the Cascadia subduction zone initiated the widespread and voluminous basaltic volcanism.[2] Some centers erupted along pre-existing brittle fault systems while volcanism along its northern portion is most widely believed to have been related to a center of upwelling magma called the Anahim hotspot (similar to that associated with present-day Hawaii), creating the Rainbow, Ilgachuz and Itcha Range shield volcanoes which also in turn form part of the Anahim Volcanic Belt. The exact nature of the relationship between the Anahim hotspot and the Chilcotin Group is, however, unknown.
Notable vents

Volcanoes of the Chilcotin Group include:
- Alixton Creek
- Browns Lake
- Crows Bar
- Prentice Gulch
- Thaddeus Lake
- Alkali Lake
- Canoe Creek
- Dog Creek
- Leon Creek
- Lambly Creek
- Missezula Lake
- Nicola (Chester)
- Quilchena Creek
- West Kettle River
- Hydraulic Lake
- Chilcotin Creek Cone
- Lightning Peak
- Black Dome Mountain
- Skoatl Point
- Alasla Mountain
- Tin Cup Mountain
- Mount Begbie
- Forestry Hill
- Lone Butte
See also
References
- ↑ Regional stratigraphy and age of Chilcotin Group basalts, south-central British Columbia Retrieved on 2012-09-22
- 1 2 National Resources Canada - Catalogue of Canadian volcanoes: Chilcotin Plateau basalts Archived March 15, 2008, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 2008-03-15