 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
2-chlorooxirane, CEO | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H3ClO | |
| Molar mass | 78.50 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Boiling point | 40–55 °C (104–131 °F; 313–328 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
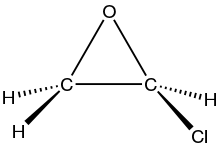
Chloroethylene oxide is the organic compound with the formula ClC2H3O. It is the epoxide of vinyl chloride. The compound is rarely observed, but it is widely proposed as a metabolite of vinyl chloride, formed by the action of cytochrome-P450. It is significant because it causes DNA alkylation. It isomerizes to chloroacetaldehyde, which modifies adenosine residues by conversion to 1,N6-ethenodeoxyadenosine (εdA).[1][2]
References
- ↑ Pandya, Gagan A.; Moriya, Masaaki (1996). "1,N6-Ethenodeoxyadenosine, a DNA Adduct Highly Mutagenic in Mammalian Cells". Biochemistry. 35 (35): 11487–11492. doi:10.1021/bi960170h. PMID 8784204.
- ↑ Clewell, Harvey J.; Gentry, P.Robinan; Gearhart, Jeffrey M.; Allen, Bruce C.; Andersen, Melvin E. (2001). "Comparison of cancer risk estimates for vinyl chloride using animal and human data with a PBPK model". Science of the Total Environment. 274 (1–3): 37–66. doi:10.1016/s0048-9697(01)00730-6. PMID 11453305. S2CID 43793528.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.