 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
methylthiomethyl chloride; MTMCl | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H5ClS | |
| Molar mass | 96.57 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.1773 g cm−3 |
| Boiling point | 107 °C (225 °F; 380 K) 750 mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H225, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P264+P265, P271, P280, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P319, P321, P332+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Dimethyl sulfide; 2-Chloroethyl ethyl sulfide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
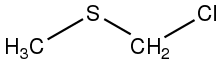
Chloromethyl methyl sulfide is the organosulfur compound with the formula ClCH2SCH3. In terms of functional groups, it is a thioether and an alkyl chloride. The compound is structurally related to sulfur mustards, i.e., it is a potentially hazardous alkylating agent. The compound finds some use in organic chemistry as a protecting group. In the presence of base, it converts carboxylic acids (RCO2H) to esters RCO2CH2SCH3.[2] The compound is prepared by treatment of dimethylsulfide with sulfuryl chloride.[3]
References
- ↑ "Chloromethyl methyl sulfide". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ↑ Tsai, Yeun-Min (2001). "Chloromethyl Methyl Sulfide". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rc119. ISBN 0471936235.
- ↑ Bordwell, F. G.; Pitt, Burnett M. (1955). "The Formation of α-Chloro Sulfides from Sulfides and from Sulfoxides". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 77 (3): 572–577. doi:10.1021/ja01608a016.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.