| C1orf162 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | C1orf162, chromosome 1 open reading frame 162 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 3588284 HomoloGene: 45482 GeneCards: C1orf162 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Chromosome 1 open reading frame 162 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C1orf162 gene. It has been found to be hypomethylated in instances of gastric cancer. [5]
Gene
The gene is located at p13.2 on chromosome 1 in humans and contains 8 exons.[6] It is 11,026 bases long and is oriented on the plus strand.[7]

mRNA
Three transcript variants have been identified. Isoform 1 is the longest transcript and encodes the longest isoform. Isoform 2 uses an alternate in-frame splice site and is shorter than isoform 1. Isoform 3 lacks an alternate in-frame exon and is shorter compared to isoform 1.[8] There are six stem loops in the 5' untranslated region and five stem loops in the 3' untranslated region.[9]
Protein
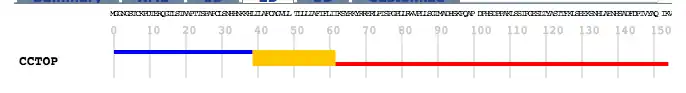
The predicted molecular weight of the protein C1orf162 is 16.9 kdal. Its isoelectric point is approximately 9.2 in mammals.[10] A single transmembrane region is conserved across species.[11] The protein is predicted to localize mainly in the nucleus.[12] The protein is predicted to be myristoylated.[13]
Expression
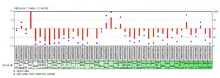
C1orf162 is not ubiquitously expressed in humans. According to microarray-assessed tissue expression patterns, C1orf162 is most highly expressed in bone marrow, lung, fetal liver, lymph node, spleen, and thymus in normal human tissues.[14] Staining of normal tissues has found high levels of RNA expression in bone marrow, lymph node, spleen, and lung tissue, which coincides with microarray-assessed expression patterns.[15]
Clinical Significance
One study found the protein to be one of three hypomethylated proteins in instances of gastric cancer.[16]
Homology
The gene has no known paralogs. Orthologs have been noted in many mammal species in addition to a few birds and reptiles. The transmembrane region of the protein is highly conserved across species. No orthologs have been identified in fish, insects, or prokaryotes.[17]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000143110 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000074342 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: Chromosome 1 open reading frame 162". Retrieved 2016-05-09.
- ↑ "NCBI GenBank". 19 March 2015.
- ↑ "GeneCards".
- ↑ "NCBI Gene".
- ↑ "M-fold Analysis".
- ↑ "SDSC Biology Workbench".
- ↑ "CCTOP".
- ↑ "PSORTII".
- ↑ "Myristoylator Prediction Program".
- ↑ "NCBI GEO".
- ↑ "Protein Atlas".
- ↑ Choi B, Han TS, Lee JY, Lee S, Kong SH, Lee HJ, Kim YJ, Yang HK (2013). "Gene methylation as a novel marker in gastric cancer". Cancer Research. 8 (73): 643. doi:10.1158/1538-7445.AM2013-643.
- ↑ "NCBI Gene Orthologs".