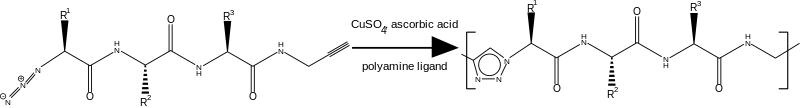
Clicked peptide polymers are poly-triazole-poly-peptide hybrid polymers. They are made of repeating units of a 1,2,3-triazole and an oligopeptide. They can be visualized as an oligopeptide that is flanked at both the C-terminus and N-terminus by a triazole molecule.
Synthesis
Clicked peptide polymers are prepared by the azide-alkyne Huisgen cycloaddition also called the click reaction; which is commonly used in bioconjugation reactions to link molecules together with a stable triazole bridge. Peptide based polymers are produced from a cycloaddition variant of step-growth polymerization. The monomers used in this polymerization are oligopeptides with terminal azide and terminal alkyne groups[1]
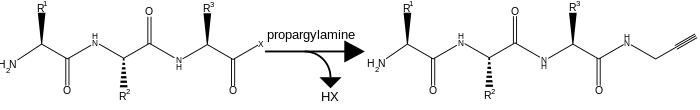
Monomer preparation
To prepare and oligopeptide with both a terminal azide and terminal alkyne two modifications must be carried out. The first is the amidation of the oligopeptide's C-terminus by propargylamine. This would done with all other reaction groups protected and with the C-terminus activated.
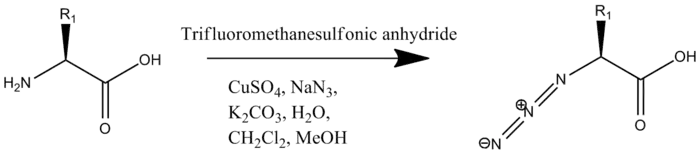
The second modification required is the addition of an azide to the N-terminus. Unlike the addition of the alkyne this can be done on the whole peptide, or solely on the N-terminal residue which is added to the rest of the oligopeptide by solid-phase peptide synthesis. The addition of the azide occurs by Cu(II)-catalyzed diazo transfer.[2]
Degradation
The molecules linked to one another by the azide-alkyne Huisgen cycloaddition are connected by an aromatic triazole which is extremely stable, and can withstand high temperatures and extremes of pH. The oligopeptide units of a clicked peptide polymer are a different story. The triazole bridges do not confer any stability to oligopeptide. Degradation of the polymer occurs at the peptide bonds linking individual amino acids. The amide bonds can be attacked non-specifically by acid or base catalyzed hydrolysis.
The polymer's peptide bonds can also be attacked by endopeptidases which will cleave at a specific side of a specific peptide bond based upon the residues which make up that bond.[1]

For example, if the first residue is a phenylalanine then the enzyme chymotrypsin will cleave at site 1, and if the third residue of the tripeptide is a lysine then trypsin would cleave at the third cleavage site.
See also
References
- 1 2 van Dijk, M., Nollet, M., Weijers, P., Dechesne, A., van Nostrum, C., Hennink, W., Rijkers, D., and Liskamp, R. (2008), Synthesis and Characterization of Biodegradable Peptide-Based Polymers Prepared by Microwave-Assisted Click Chemistry. Biomacromolecules, 10: 2834-2843
- ↑ Alper, P. B.; Hung, S.-C.; Wong, C.-H. Tetrahedron Lett. (1996), 37, 6029-6032