 Cocoamide MEA | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-(2-hydroxyethyl)dodecanamide | |
| Other names
Cocamide monoethanolamine; Monoethanolamine coconut acid amide; Coco monoethanolamide; Coconut fatty acid monoethanolamide; Cocoyl monoethanolamine; N-(2-Hydroxyethyl) coco fatty acid amide; Coconut oil fatty acid ethanolamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.062.500 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
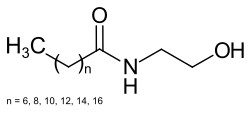
| CH3(CH2)nCONHCH2CH2OH | |
| Density | 1.08-1.09 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 60 to 63 °C (140 to 145 °F; 333 to 336 K) |
| Boiling point | > 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
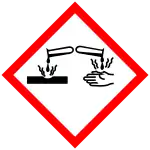   | |
| Danger | |
| H315, H318 | |
| P264, P270, P273, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P330, P332+P313, P362, P391, P501 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
> 3000 mg/kg (oral, rat)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Cocamide MEA, or cocamide monoethanolamine, is a solid, off-white to tan compound, often sold in flaked form. The solid melts to yield a pale yellow viscous clear liquid. It is a mixture of fatty acid amides which is produced from the fatty acids in coconut oil when reacted with ethanolamine.
Uses
Cocamide MEA and other cocamide ethanolamines such as cocamide DEA are used as foaming agents and nonionic surfactants in shampoos and bath products, and as emulsifying agents in cosmetics.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Cocamide MEA, chemicalland21.com
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.