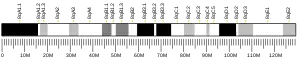| DRC7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | DRC7, C16orf50, CCDC135, CFAP50, FAP50, Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 135, dynein regulatory complex subunit 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 2685616 HomoloGene: 12996 GeneCards: DRC7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 135, also known as CCDC135, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCDC135 gene.[5][6]
Gene
CCDC90B is located on chromosome 16 in humans. It is neighbored by:[7]
- GPR97, G protein-coupled receptor 97.
- GPR56, encodes a member of the G protein coupled receptor family (G protein-coupled receptor 56). The gene is implicated in the regulation of brain cortical patterning. The protein binds specifically to transglutaminase 2 in the extracellular space.
- KATNB1, katanin p80 subunit B 1. An accessory protein that helps targets the enzyme to the centrosome.
- KIFC3, kinesin family member C3 isoform 3. KIFC3 belongs to the large superfamily of kinesins, molecular motors that use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to translocate cargoes along microtubules.
Protein
Structure
This protein is characterized by the presence of two domains.[8]
- Nuclear localization sequence with a Score of 4 in the amino acids 265–279. The amino acid sequence for this region is:
KKQQEIRAQEKKRLR
- Transglutaminase-like family with an E Value of 0.0018 in the amino acids 149–308. The amino acid sequence for this region is:
CAQFVSDFLTMVPLPDPLKPPSHLYSSTTVLKYQKGNCFDFSTLLCSMLIGSGYDAYCVNGYGSLDLCHMDLTREVCPLTVKPKETIKKEEK VLPKKYTIKPPRDLCSRFEQEQEVKKQQEIRAQEKKRLREEEERLMEAEKAKPDALHGLRVHSWVLVL
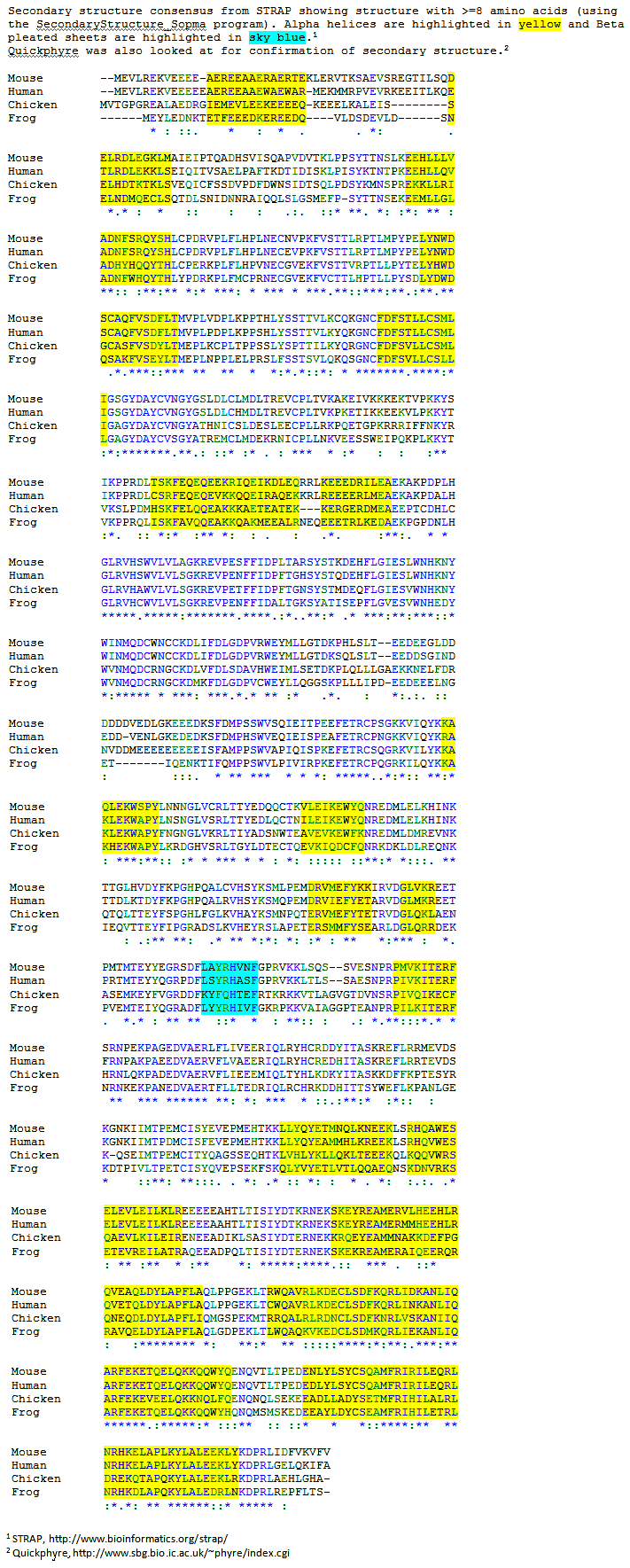
The protein has 17 predicted alpha helices sites, a characteristic of coiled-coil proteins, and 1 predicted beta-pleated sheet. The following image shows the predicted regions of alpha helices and beta pleated sheets by two programs STRAP[9] and Quickphyre:[10] Note: the consensus secondary structures are shown. This was carried out by constructing a multiple sequence alignment of the proteins with their secondary structures (as shown below). The predicted regions were then cross checked with the Quickphyre Archived 30 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine Program.
Homology
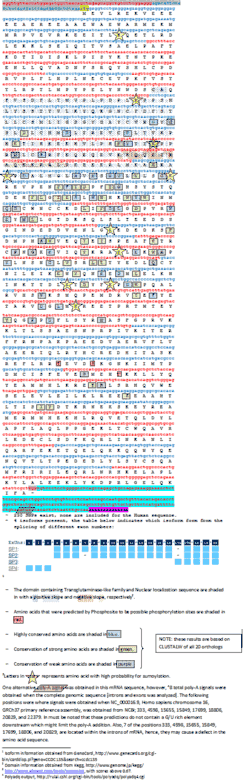
LRRC57 is exceedingly well conserved, as shown in the sequence annotation to the right. The sequence annotation was created using 20 orthologs shown in the table below and was prepared using ClustalX2[11] and ClustalW (a tool at Biology Workbench).[12]
The following table provides a few details on orthologs of the human version of CCDC135. These orthologs were gathered from BLAT.[13] and BLAST searches[14]
| Species | Organism common name | NCBI accession | Sequence identity | Sequence similarity | Length (AAs) | Gene common name |
| Homo sapiens | Human | NP_115645.4 | 100% | 100% | 874 | Homo sapiens coiled-coil domain containing 135 (CCDC135) |
| Macaca mulatta | Rhesus monkey | XP_001100628.1 | 96% | 98% | 830 | Predicted: similar to chromosome 16 open reading frame 50 |
| Bos taurus | Cow | NP_001033120.1 | 86% | 93% | 872 | coiled-coil domain-containing protein 135 |
| Canis familiaris | Dog | XP_544386.2 | 85% | 92% | 903 | Predicted: similar to chromosome 16 open reading frame 50 |
| Equus caballus | Horse | XP_001915581 | 81% | 87% | 831 | Predicted: similar to Coiled-coil domain containing 135 |
| Rattus norvegicus | Rat | NP_001099639 | 84% | 91% | 874 | hypothetical protein LOC291853 |
| Mus musculus | Mouse | NP_001036180 | 82% | 90% | 876 | coiled-coil domain containing 135 |
| Ornithorhynchus anatinus | Platypus | XP_001508368.1 | 71% | 85% | 860 | Predicted: similar to Coiled-coil domain containing 135 |
| Monodelphis domestica | Opossum | XP_001363193.1 | 70% | 84% | 866 | Predicted: hypothetical protein isoform 1 |
| Gallus gallus | Chicken | XP_425101.2 | 57% | 72% | 868 | Predicted: hypothetical protein |
| Taeniopygia guttata | Zebra finch | XP_002195392.1 | 50% | 67% | 731 | Predicted: hypothetical protein |
| Xenopus troicalis | Frog | NP_001072331.1 | 56% | 71% | 856 | coiled-coil domain containing 135 |
| Danio rerio | Zebrafish | XP_683491 | 46% | 66% | 721 | Predicted: similar to Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 135 |
| Tetraodon nigroviridis | Tetraodon | CAG07272 | 42% | 59% | 526 | unnamed protein product |
| Nematostella vectensis | Sea anemone | XP_001632291 | 53% | 70% | 817 | predicted protein |
| Branchiostoma floridae | Lancelet | XP_002610594 | 51% | 71% | 850 | hypothetical protein BRAFLDRAFT_275841 |
| Ciona intestinalis | Sea squirt | XP_002123665 | 49% | 69% | 837 | Predicted: similar to coiled-coil domain containing 135 |
| Anopheles gambiae | Mosquito | XP_312247.4 | 32% | 49% | 662 | AGAP002677-PA |
| Nasonia vitripennis | Wasp | XP_001607094 | 34% | 55% | 868 | Predicted: hypothetical protein |
| Drosophila melanogaster | Fruit fly | NP_001036757.1 | 28% | 47% | 897 | CG34110 |
Predicted properties
- Molecular weight: 103502.53 = 103484.53 + 18 kDa
- Isoelectric point: 5.358000
- Transmembrane helices: None
- Post-translation modifications:[15]
- Chloroplast transit peptides: None
- Signal pepties: Yes [8]
- Nuclear Localization Sequence: KKQQEIRAQEKKRLR
- C-mannosylation sites: None (However, 14 sites with scores lower than the threshold were predicted.[16])
- Mitochondrial targeting: None
- N-glycosylation sites: Yes
- Sequence gi|223941912 at positions 100 and 493 with potentials of 0.7200 and 0.6031 receptively.
Cellular location
CCDC135 is predicted to be a Cytosol/Nuclear protein[17] with no transmembrane spans or segments. It is predicted to contain at least 56 specific phosphorylation sites[18] which include: 20 Protein Kinase C Phosphorylation sites, 11 Casein Kinase II Phosphorylation sites, and 8 cAMP/cGMP Dependent Phosphorylation sites. The amino acid sequence is also predicted to contain 10 sumoylation[19] sites at positions K236, K236, K45, K773, K499, K679, K249, K167, K540, K445, and K292.
Function
The function of CCDC135 is not yet well understood but it is thought to be involved in teratospermia.
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000159625 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000031786 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, Gassenhuber J, Glassl S, Ansorge W, Böcher M, Blöcker H, Bauersachs S, Blum H, Lauber J, Düsterhöft A, Beyer A, Köhrer K, Strack N, Mewes HW, Ottenwälder B, Obermaier B, Tampe J, Heubner D, Wambutt R, Korn B, Klein M, Poustka A (March 2001). "Toward a catalog of human genes and proteins: sequencing and analysis of 500 novel complete protein coding human cDNAs". Genome Res. 11 (3): 422–35. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072. PMID 11230166.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: coiled-coil domain containing 135".
- ↑ "Human hg38 chr16%3A56276931-56332628 UCSC Genome Browser v420".
- 1 2 "Kegg T01001: 84229".
- ↑ "Multiple sequence alignment: Strap".
- ↑ "Redirecting to Phyre2". Archived from the original on 30 April 2017. Retrieved 9 May 2010.
- ↑ "Clustal Home Page". Retrieved 4 May 2009.
- ↑ "Home". workbench.sdsc.edu.
- ↑ "BLAT Search Genome". Retrieved 4 May 2009.
- ↑ "BLAST". Retrieved 4 May 2009.
- ↑ "ExPASy". SIB Switzerland. 5 January 2009. Retrieved 14 May 2009.
- ↑ "NetCGlyc 1.0 Server".
- ↑ "PSORT II Prediction". Archived from the original on 29 March 2009. Retrieved 9 May 2010.
- ↑ "NetPhosK 1.0 Server". Archived from the original on 9 July 2021. Retrieved 9 May 2010.
- ↑ "SUMOplot™ Analysis Program | Abcepta".