| Type | transport, law of the sea |
|---|---|
| Signed | 8 July 1965 |
| Location | New York City, United States |
| Effective | 9 June 1967 |
| Condition | ratification by two land-locked states and two states with a sea coast |
| Signatories | 27 |
| Parties | 43 |
| Depositary | Secretary-General of the United Nations |
| Languages | English, French, Russian, Chinese, and Spanish |
The Convention on Transit Trade of Land-locked States is a multilateral treaty that addresses international rules allowing for land-locked countries to transport goods to and from seaports. The convention imposes obligations on both land-locked states and on coastal states that ratify the treaty.
The convention was concluded at the United Nations Conference on Transit Trade of Land-locked Countries, which had been established by the United Nations General Assembly. It was concluded and signed on 8 July 1965. The treaty came into force on 9 June 1967.
Coastal states that ratify the convention (known as "transit states")[1] agree to make arrangements with land-locked states that are party to the treaty that wish to transit goods across the territory of the transit state to or from a coastal port in the transit state. The transit states agree that they will not discriminate based on place of origin or destination of the goods being transported. The land-locked states agree to be responsible for any expenses that the transit states incur in supervising or protecting the transit of the land-locked state's goods.
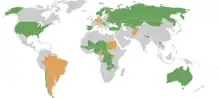
The convention has been noted as the first international agreement to recognise the special disadvantaged position of land-locked states.[2]
As of June 2014, the treaty has been ratified by 43 states, made up of an approximately even split of land-locked and coastal states. The convention has essentially been superseded by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, which contains similar provisions for transit arrangements to be made between coastal and land-locked states.
Notes
References
- Kishor Uprety, The Transit Regime for Landlocked States: International Law and Development Perspectives (Washington DC: The World Bank, 2006, ISBN 9780821362990) pp. 66–75.