Core frame model
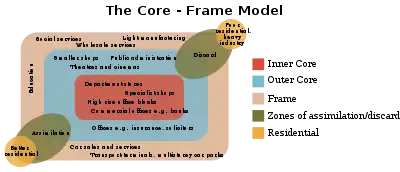
The Core frame model is a model showing the urban structure of the Central Business District of a town or city. The model was first suggested by Ronald R. Boyce and Edgar M. Horwood in 1959.[1]
The model includes an inner core where land is expensive and used intensively, resulting in vertical development. This area is the focus of the transport system and has a concentrated daytime population. The outer core and frame have lower land values and are less intensively developed.[2] The various land uses are linked to the bid rent theory. The zone of assimilation and zone of discard are together called the zone of transition.
See also
Notes
Further reading
- Waugh, David Geography: An Integrated Approach 1995
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.