| coronadite | |
|---|---|
 Coronadita | |
| General | |
| Category | hydroxides |
| Formula (repeating unit) | Pb(Mn4+6Mn3+2)O16 |
| IMA symbol | Cor[1] |
| Strunz classification | 4/D.08-70 |
| Dana classification | 7.9.1.4 |
| Crystal system | monoclinic |
| Space group | I2/m |
| Unit cell | a = 9.938, b = 2.8678, c = 9.834, Z = 1; β = 90.39° V = 280.26 |
| Identification | |
| Formula mass | 933.55 |
| Colour | dark grey to black |
| Crystal habit | botryoidal; fibrous |
| Mohs scale hardness | 4.5–5 |
| Luster | submetallic |
| Streak | brownish black |
| Diaphaneity | opaque |
| Density | 5.44 |
| Refractive index | 2.72? |
| Pleochroism | brown-grey |
| Common impurities | Fe, Al |
Coronadite is the lead endmember of the hollandite group, a family of tectomanganates with a 2 × 2 tunnel structure. The mineral was named after Francisco Vasquez de Coronado who was an explorer of southwest US. The name was made up by Waldemar Lindgren in 1905.[2]
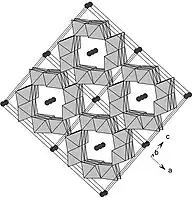 Polyhedral representation of the 2 × 2 tunnel structure of coronadite. The black atoms represent Pb.
Polyhedral representation of the 2 × 2 tunnel structure of coronadite. The black atoms represent Pb.
References
- ↑ Warr, L.N. (2021). "IMA–CNMNC approved mineral symbols". Mineralogical Magazine. 85 (3): 291–320. Bibcode:2021MinM...85..291W. doi:10.1180/mgm.2021.43. S2CID 235729616.
- ↑ "Coronadite Mineral Data". webmineral.com.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.