 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
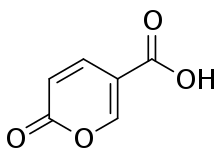
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Oxo-2H-pyran-5-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Cumalic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.182 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 140.094 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 210 °C (410 °F; 483 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Coumalic acid is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H4O4. Its melting point is around 210 °C.
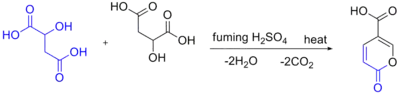
In laboratory coumalic acid may be obtained by self-condensation of malic acid in fuming sulfuric acid:[1]
Note that this scheme is incorrect. 4 H2O and 2 CO (carbon monoxide, not carbon dioxide) are liberated during the condensation.
References
- ↑ Richard H. Wiley and Newton R. Smith (1963). "Coumalic acid". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, vol. 4, p. 201
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.