| Cruciform eminence | |
|---|---|
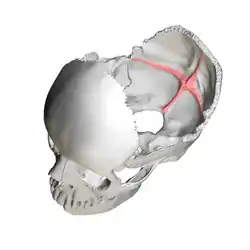 Human skull. Position of cruciform eminence is shown in red. | |
 Occipital bone. Inner surface. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Eminentia cruciformis |
| TA98 | A02.1.04.028 |
| TA2 | 574 |
| FMA | 75754 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The cruciform eminence (or cruciate eminence) divides the deeply concave internal surface of the occipital bone into four fossae:
- The upper two fossae are called the cerebral fossae, are triangular and lodge the occipital lobes of the cerebrum.
- The lower two are called the cerebellar fossae, are quadrilateral and accommodate the hemispheres of the cerebellum.
The upper fossae are separated from the lower fossae by a groove for the transverse sinuses. At the point of intersection between all four fossae is the internal occipital protuberance.
Additional images
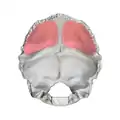 Cerebral fossa (shown in red)
Cerebral fossa (shown in red)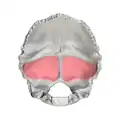 Cerebellar fossa (shown in red)
Cerebellar fossa (shown in red)
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 130 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 130 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cruciform eminence.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.