 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
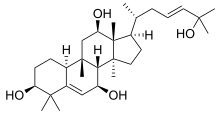
| IUPAC name
(23E)-9-Methyl-19-nor-9β,10α-lanosta-5,23-diene-3β,7β,12β,25-tetrol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,3aS,3bR,4S,7S,9aS,9bS,11R,11aR)-1-[(2R,4E)-6-Hydroxy-6-methylhept-4-en-2-yl]-3a,6,6,9b,11a-pentamethyl-2,3,3a,3b,4,6,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-4,7,11-triol | |
| Other names
Cucurbita-(5,23E)-diene-3β,12β,25-triol; (3β,7β,9β,10α,12β,23E)-4,4,9,14-tetramethyl-19-norcholesta-5,23-diene-3,7,12,23-diol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H50O4 | |
| Molar mass | 474.726 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Cucurbalsaminol A or cucurbita-5,23(E)-diene-3β,12β,25-triol, is a chemical compound with formula C
30H
50O
4, found in the Balsam apple vine (Momordica balsamina). It is a cucurbitane-type triterpenoid, related to cucurbitacin, isolated by C. Ramalhete and others in 2009.[1]
Cucurbalsaminol A is an amorphous powder soluble in methanol and ethyl acetate but insoluble in n-hexane. Unlike Cucurbalsaminol B, it is not cytotoxic.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 Cátia Ramalhete; Tayyab A. Mansoor; Silva Mulhovo; Joseph Molnár; Maria-José U. Ferreira (2009). "Cucurbitane-Type Triterpenoids from the African Plant Momordica balsamina". Journal of Natural Products. 72 (11): 2009–2013. doi:10.1021/np900457u. hdl:10884/1322. PMID 19795842.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.