 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.975 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 100.117 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Melting point | −7.5 °C (18.5 °F; 265.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 191.5–193.5 °C (376.7–380.3 °F; 464.6–466.6 K) 740 mm |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
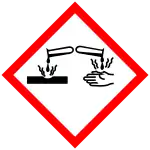  | |
| Danger | |
| H302, H312, H314, H332 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P317, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P302+P361+P354, P304+P340, P305+P354+P338, P316, P317, P321, P330, P362+P364, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
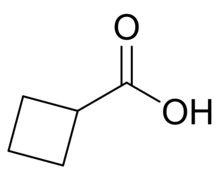
Cyclobutanecarboxylic acid is the organic compound with the formula C4H7CO2H. It is a colorless nonvolatile liquid. It can be prepared by decarboxylation of 1,1-cyclobutanedicarboxylic acid.[2] Cyclobutanecarboxylic acid is an intermediate in organic synthesis. For example, it is a precursor to cyclobutylamine.[3]
References
- ↑ "Cyclobutanecarboxylic acid". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ↑ "1,1-Cyclobutanedicarboxylic Acid and Cyclobutanecarboxylic Acid". Organic Syntheses. 23: 16. 1943. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.023.0016.
- ↑ Newton W. Werner, Joseph Casanova, Jr. (1967). "Cyclobutylamine". Organic Syntheses. 47: 28. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.047.0028.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.