 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.219 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H14O | |
| Molar mass | 126.199 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Melting point | 42 °C (108 °F; 315 K) |
Refractive index (nD) |
0.959 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
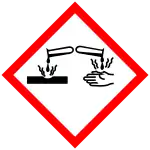  | |
| Danger | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P264+P265, P271, P280, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P302+P361+P354, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P305+P354+P338, P316, P319, P321, P332+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Cyclooctanone is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)7CO. It is a waxy white solid.
Synthesis
- It can be prepared by Jones oxidation of cyclooctanol.
- It can also be produced by ketonization reaction starting with azelaic acid.[2]
Use
Use of cyclooctanone is almost nonexistent drug chemistry with only 2 known exceptions:
See also
References
- ↑ "Cyclooctanone". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ↑ E. J. Eisenbraun (1965). "Cycloöctanone". Organic Syntheses. 45: 28. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.045.0028.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.