 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2-Dibromo-2-cyanoacetamide[1] | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.477 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| MeSH | 2,2-dibromo-3-nitrilopropionamide | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1759 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H2Br2N2O | |||
| Molar mass | 241.870 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White, translucent crystals | ||
| Melting point | 122 to 125 °C (252 to 257 °F; 395 to 398 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
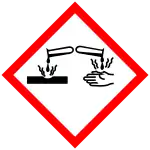   | |||
| Danger | |||
| H314, H317, H400 | |||
| P273, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose) |
10 mg kg−1 (intravenous, mouse) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
Cyanoacetamide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
DBNPA or 2,2-dibromo-3-nitrilopropionamide is a quick-kill biocide that easily hydrolyzes under both acidic and alkaline conditions. It is preferred for its instability in water as it quickly kills and then quickly degrades to form a number of products, depending on the conditions, including ammonia, bromide ions, dibromoacetonitrile, and dibromoacetic acid.[2] DBNPA acts similar to the typical halogen biocides.
DBNPA is used in a wide variety of applications. Some examples are in papermaking as a preservative in paper coating and slurries. It is also used as slime control on papermachines, and as a biocide in hydraulic fracturing wells and in cooling water.[2]
References
- ↑ "2,2-dibromo-3-nitrilopropionamide - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification. Retrieved 9 June 2012.
- 1 2 "Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) 2,2-dibromo-3-nitrilopropionamide (DBNPA)" (PDF). "EPA 738-R-94-026". US EPA. September 1994. p. 179. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-16. Retrieved 2012-06-14.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.