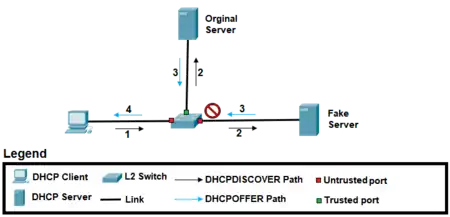
Example showing how DHCP snooping works
In computer networking, DHCP snooping is a series of techniques applied to improve the security of a DHCP infrastructure.[1]
DHCP servers allocate IP addresses to clients on a LAN. DHCP snooping can be configured on LAN switches to exclude rogue DHCP servers and remove malicious or malformed DHCP traffic. In addition, information on hosts which have successfully completed a DHCP transaction is accrued in a database of bindings which may then be used by other security or accounting features.[2][3]
Other features may use DHCP snooping database information to ensure IP integrity on a Layer 2 switched domain. This information enables a network to:
References
- ↑ Banks, Ethan. "Five Things To Know About DHCP Snooping". Packet Pushers. Retrieved 29 February 2016.
- ↑ "What Is DHCP Snooping, all things you should know". Leslie. Retrieved 22 March 2023.
- ↑ "DHCP Snooping". Adarsh Sahni. 14 July 2020.
- ↑ Cisco Systems, Inc. "Catalyst 3750-X and Catalyst 3560-X Switch Software Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2)SE and Later". Cisco.com. Retrieved 29 February 2016.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.