| DHRS1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | DHRS1, SDR19C1, dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 1, dehydrogenase/reductase 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 610410 MGI: 1196314 HomoloGene: 41696 GeneCards: DHRS1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dehydrogenase/reductase SDR family member 1, also known as Short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family 19C member 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DHRS1 gene located on chromosome 14.[5][6][7]
Structure
The DHRS1 gene is located on the chromosome 14q21.3 region and contains 9 exons. It encodes a 314-amino-acid, 33-kDa protein that is thought to be located to the endoplasmic reticulum and the mitochondrial inner membrane inside the cell.
Function
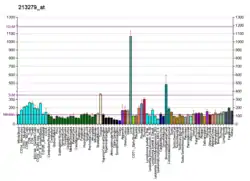
The DHRS1 protein is thought to have oxidoreductase activity based on sequence similarity and conserved catalytic sites with other short-chain oxidoreductase enzymes. The enzyme is found to be expressed in the fetal brain.[8]
Interactions
The DHRS1 protein is thought to interact with the protein phospholipid scrambase 1 (PLSCR1).[9]
References
- 1 2 3 ENSG00000284868 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000157379, ENSG00000284868 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000002332 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Wu Q, Xu M, Cheng C, Zhou Z, Huang Y, Zhao W, Zeng L, Xu J, Fu X, Ying K, Xie Y, Mao Y (Aug 2002). "Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel Dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 1 genea from human fetal brain". Mol Biol Rep. 28 (4): 193–8. doi:10.1023/A:1015722001960. PMID 12153138. S2CID 29552121.
- ↑ Persson B, Kallberg Y, Bray JE, Bruford E, Dellaporta SL, Favia AD, Duarte RG, Jornvall H, Kavanagh KL, Kedishvili N, Kisiela M, Maser E, Mindnich R, Orchard S, Penning TM, Thornton JM, Adamski J, Oppermann U (Feb 2009). "The SDR (Short-Chain Dehydrogenase/Reductase and Related Enzymes) Nomenclature Initiative". Chem Biol Interact. 178 (1–3): 94–8. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2008.10.040. PMC 2896744. PMID 19027726.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: DHRS1 dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 1".
- ↑ Wu Q, Xu M, Cheng C, Zhou Z, Huang Y, Zhao W, Zeng L, Xu J, Fu X, Ying K, Xie Y, Mao Y (2001). "Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel Dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 1 genea from human fetal brain". Mol. Biol. Rep. 28 (4): 193–8. doi:10.1023/A:1015722001960. PMID 12153138. S2CID 29552121.
- ↑ "IntAct Portal".
Further reading
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (2001). "DNA Cloning Using In Vitro Site-Specific Recombination". Genome Res. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863.
- Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, et al. (2001). "Toward a Catalog of Human Genes and Proteins: Sequencing and Analysis of 500 Novel Complete Protein Coding Human cDNAs". Genome Res. 11 (3): 422–35. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072. PMID 11230166.
- Simpson JC, Wellenreuther R, Poustka A, et al. (2001). "Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing". EMBO Rep. 1 (3): 287–92. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058. PMC 1083732. PMID 11256614.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Wiemann S, Arlt D, Huber W, et al. (2004). "From ORFeome to Biology: A Functional Genomics Pipeline". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2136–44. doi:10.1101/gr.2576704. PMC 528930. PMID 15489336.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Mehrle A, Rosenfelder H, Schupp I, et al. (2006). "The LIFEdb database in 2006". Nucleic Acids Res. 34 (Database issue): D415–8. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj139. PMC 1347501. PMID 16381901.