The DeMayo reaction is a photochemical reaction in which the enol of a 1,3-diketone reacts with an alkene (or another species with a C=C bond) and the resulting cyclobutane ring undergoes a retro-aldol reaction to yield a 1,5-diketone:[1]
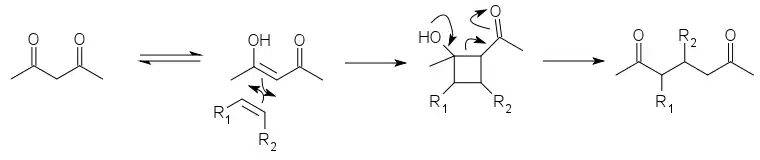
The net effect is to add the two carbon atoms in the C=C double bond between the two carbonyl groups of the diketone. It is thus useful in syntheses both as a relatively selective way to join two parts of a molecule and as a way to apply the more developed chemistry of 1,3-diketone synthesis to 1,5-diketones. The first part is a [2+2] cycloaddition. The ensuing retro-aldol cleavage is favored by the relative instability of the cyclobutane ring.
 |
| An animation of the reaction mechanism |
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.