 The engine after it experienced catastrophic uncontained compressor rotor failure | |
| Accident | |
|---|---|
| Date | July 6, 1996 |
| Summary | Uncontained engine failure |
| Site | Runway 17 at Pensacola Regional Airport, Pensacola, Florida, United States 30°28′40″N 87°11′25″W / 30.47778°N 87.19028°W |
| Aircraft | |
| Aircraft type | McDonnell Douglas MD-88 |
| Operator | Delta Air Lines |
| Registration | N927DA |
| Flight origin | Pensacola Regional Airport, Pensacola, Florida |
| Destination | William B. Hartsfield International Airport, Atlanta, Georgia |
| Occupants | 142 |
| Passengers | 137 |
| Crew | 5 |
| Fatalities | 2 |
| Injuries | 7 |
| Survivors | 140 |
Delta Air Lines Flight 1288 was a regularly scheduled flight from Pensacola, Florida to Atlanta, Georgia. On July 6, 1996, the aircraft serving the flight, a McDonnell Douglas MD-88, was on takeoff roll from Runway 17 at Pensacola when it experienced an uncontained, catastrophic turbine engine failure that caused debris from the front compressor hub of the left engine to penetrate the left aft fuselage. The cause of the engine failure was found to have been a fault in the manufacture of the fan. The failure of the airline to spot the resulting crack in the blade was a contributing factor.
The impact killed a female passenger and her son, and seven other passengers were injured. The pilot aborted takeoff and the airplane stopped on the runway. Three other passengers sustained minor injuries during the emergency evacuation. Most of the passengers were traveling on vacation.[1]
Aircraft and crew
The aircraft involved was an eight-year-old McDonnell Douglas MD-88 registered as N927DA.[2] It was built in April 1988 and delivered to Delta in November that same year. The aircraft was equipped with two Pratt & Whitney JT8D-219 turbofan engines. It had accrued 22,031 flight hours and 18,826 takeoff and landing cycles.[3]: 8–13
The captain was 40-year-old John Ray Bunnell, who had been with Delta Air Lines since 1979, having previously flown for a commuter airline. He had 12,000 flight hours of experience, including 2,300 hours on the MD-88. The first officer was 37-year-old former Air Force pilot David William Hawk, who had been with Delta since 1990, having logged 6,500 flight hours, 500 of which were on the MD-88.[3]: 6–8 [4]
Pre-flight inspection
During a 15-minute walkthrough pre-flight inspection,[5] the first officer noted a few drops of oil coming from the "bullet" or tip of the number one (left) engine, although it was said to be "not that serious." The first officer also noticed a couple of missing rivets on the left wing. The pilot told National Transportation Safety Board investigators that neither problem was considered dangerous and that the aircraft was airworthy; therefore, maintenance was not informed.[3]
Takeoff and accident
.jpg.webp)
At 2:23 pm CDT, Delta flight 1288 was cleared for takeoff on Runway 17. The aircraft was filled to capacity with passengers.[5]
As the first officer was advancing the throttles and reaching an airspeed of 40 knots (74 km/h; 46 mph), the rear-cabin passengers and flight crew heard a very loud banging noise and experienced a blast-like sensation. Many of the passengers at the front of the cabin believed that the airplane may have blown a tire. Nearby witnesses observed a large fireball, and one had noticed the left engine hanging low seconds before the explosion. Passengers observed pieces of metal that were violently propelled through the cabin, and the rear of the plane filled with smoke. Despite the initial fireball, the aircraft did not sustain a fire. Some parts of the plane were propelled as far as a half of a mile away.[5]
The cockpit lost lighting and instrumentation and the pilot ended the takeoff by bringing the throttle to idle and engaging the brake, which brought the aircraft to an eventual stop without use of reversers or spoilers.[3]
When the aircraft stopped, the first officer unsuccessfully attempted to contact the tower, but the cockpit had lost power. The flight crew then activated emergency power, contacted the tower and declared an emergency. A deadheading Delta pilot sitting in the cockpit's jump seat went to inspect the rear of the aircraft. When the first officer saw the over-wing exits open and about half of the passengers missing along with hearing engine noise, he returned to the cockpit and advised the captain to disable the engines.

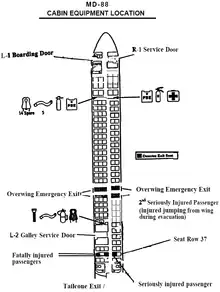
At 2:27 pm CDT, the pilot requested emergency medical assistance after learning of the large hole in the fuselage, engine debris throughout the cabin and injured passengers. He then reported that there was no evidence of smoke or fire in the cabin and that the rear-cabin door had been opened and the emergency slide was inflated. The flight attendant who initiated the evacuation through the door told the NTSB that she saw fire on the left engine and therefore abandoned evacuation through that door and directed passengers forward. She reported that as there were many injuries and possibly two dead, she began to evacuate the plane until she was stopped by the first officer. Because of the damage to the rear of the aircraft, the plane's stairs were found unsuitable for use. The captain requested portable air stairs, which arrived 25 minutes later.[3] Many passengers escaped through the emergency exits over the wings and then jumped to the ground or slid down chutes.[5]
An escaping passenger noted: "When we finally got out, we looked over there and saw the rotary blades out of the jet motor had blown and sheared the plane just like a can opener."[5]
Injuries and deaths
Passenger Anita Saxton, 36, and her twelve-year-old son Nolan, who had been seated in Row 37 near the rear of the aircraft, were killed instantly when stuck by flying fragments of metal.[6] Two of Saxton's other children were injured. A total of seven passengers were hospitalized, two of whom received serious injuries; one resulted from the initial event and the other from jumping from the wing during evacuation.[7][5]
NTSB investigation
After a comprehensive investigation, the NTSB determined the most probable cause of the accident to be a fracture in the left engine's front compressor fan hub that resulted from failure of the airline's fluorescent penetrant inspection process to detect a potentially dangerous crack in the fan originating with the engine's initial manufacture.[3]
Aftermath
The aircraft involved in the accident was repaired and returned to service with Delta under the same registration, N927DA.[8][9] The aircraft was withdrawn from service on August 10, 2018.[10]
See also
- Delta Air Lines Flight 1086 – A 2015 accident involving another MD-88, without fatalities
- Southwest Airlines Flight 1380 – A 2018 similar accident, with one fatality
- Southwest Airlines Flight 3472 – A 2016 similar accident, without fatalities
- British Airtours Flight 28M, a Boeing 737 that abandoned takeoff after a combustor explosion in 1985, killing 55.
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Transportation Safety Board.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Transportation Safety Board.
- ↑ "2 die when engine shatters as jet takes off". Houston Chronicle. Houston Chronicle News Services. July 7, 1996. p. A1. Archived from the original on May 11, 2009. Retrieved February 13, 2009.
- ↑ "FAA Registry (N927DA)". Federal Aviation Administration.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Uncontained Engine Failure, Delta Air Lines Flight 1288, McDonnell Douglas MD-88, N927DA, Pensacola, Florida, July 6, 1996" (PDF). www.ntsb.gov. National Transportation Safety Board. January 13, 1998. Retrieved December 27, 2018.
- ↑ "Operations 2 -Exhibit No. 2A - Group Chairman Factual Report - Operational Factors/Human Performance" (PDF). National Transportation Safety Board. Retrieved April 14, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Graybiel, Ginny (July 6, 1996). "Delta engine blows apart, killing 2, but 145 survive". Pensacola News Journal. p. 1.
- ↑ Wald, Matthew L. (July 7, 1996). "2 Killed in Jet On Runway After Engine Breaks Apart". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved January 13, 2014.
- ↑ "2 Killed as Engine Parts Pierce Cabin of Delta Jet". Los Angeles Times. June 27, 1985. Retrieved January 13, 2014.
- ↑ "FAA Registry (N927DA)". Federal Aviation Administration.
- ↑ "FAA Registry - Aircraft - N-Number Inquiry". registry.faa.gov. Federal Aviation Administration. Archived from the original on July 21, 2018. Retrieved February 27, 2020.
- ↑ "N927DA Delta Air Lines McDonnell Douglas MD-88". www.planespotters.net. Retrieved July 11, 2020.