 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2H5)Ethan(2H)ol | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.693 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2D6O | |
| Molar mass | 52.10 g/mol |
| Density | 0.892 g/mL[1] |
| Boiling point | 78 °C (172 °F; 351 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
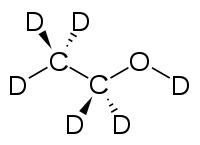
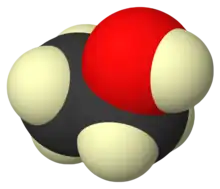
Deuterated ethanol (C2D5OD)[2] is a form (called an isotopologue) of ethanol (C2H5OH) in which the hydrogen atom ("H") is replaced with deuterium (heavy hydrogen) isotope ("D"). Deuterated ethanol is an uncommon solvent used in NMR spectroscopy.
References
- 1 2 "Ethanol-d6". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ↑ March, Raymond E.; Todd, John F. J. (2010). Practical Aspects of Trapped Ion Mass Spectrometry: Applications of Ion Trapping Devices. CRC Press. p. 38. ISBN 978-1-4200-8373-6.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.