In organic chemistry, diazines are a group of organic compounds having the molecular formula C4H4N2. Each contains a benzene ring in which two of the C-H fragments have been replaced by isolobal nitrogen.[1] There are three structural isomers:
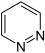
- pyridazine (1,2-diazine)
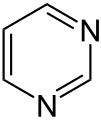
- pyrimidine (1,3-diazine)
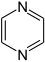
- pyrazine (1,4-diazine)
See also
- 6-membered rings with one nitrogen atom: pyridines
- 6-membered rings with three nitrogen atoms: triazines
- 6-membered rings with four nitrogen atoms: tetrazines
- 6-membered rings with five nitrogen atoms: pentazines
- 6-membered rings with six nitrogen atoms: hexazines
References
- ↑ Lin-Vien, Daimay; Colthup, Norman B.; Fateley, William G.; Grasselli, Jeanette G. (1991-01-01). "Aromatic and Heteroaromatic Rings". The Handbook of Infrared and Raman Characteristic Frequencies of Organic Molecules. Academic Press. pp. 277–306. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-057116-4.50023-7. ISBN 978-0-12-451160-6.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.