| |||
anthracene-3D-spacefill.png.webp) | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
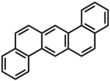
Benzo[k]tetraphene | |||
| Other names
1,2:5,6-Dibenzanthracene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.166 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 3077 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C22H14 | |||
| Molar mass | 278.354 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.232 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 262 °C (504 °F; 535 K)[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  | |||
| Danger | |||
| H350, H410 | |||
| P201, P202, P273, P281, P308+P313, P391, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Dibenz[a,h]anthracene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C22H14. It is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) made of five fused benzene rings. It is a fused five-ringed PAH which is common as a pollutant of smoke and oils. It is white to light yellow crystalline solid. It is stable and highly genotoxic in bacterial and mammalian cell systems, as it intercalates into DNA and causes mutations.
It was first synthesized in 1918.[1]
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
anthracene-3D-balls.png.webp)