| Dibranchus atlanticus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Lophiiformes |
| Family: | Ogcocephalidae |
| Genus: | Dibranchus |
| Species: | D. atlanticus |
| Binomial name | |
| Dibranchus atlanticus W. K. H. Peters, 1876 [2] | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Halieutaea senticosa Goode, 1881[2] | |
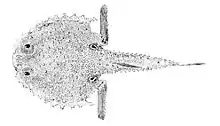
The Atlantic batfish (Dibranchus atlanticus)[3] is a species of fish in the family Ogcocephalidae. It is found in deep water in the Atlantic Ocean where it lives on the seabed, feeding on small invertebrates.
Description
D. atlanticus has a disc-shaped, vertically compressed body with a flat ventral surface, and grows to a standard length of 145 mm (6 in). The dorsal fin, which is set far back near the tail, has no spines and five to seven soft rays, and the anal fin has no spines and four soft rays. The pectoral fins are robust and held at right angles to the body; they are limb-like and are used to "walk" over the seabed, and the more slender pelvic fins serve the same purpose.[4] Under the operculum there is a sturdy multi-pointed spine. The bases of the fins, apart from the dorsal fin, are decorated with tubercles (cone-shaped scales) and the ventral surface of the disc is covered by distinct scales. The dorsal surface of the fish is usually a uniform reddish-grey, but specimens in the eastern Atlantic sometimes have reticulated markings. The ventral surface is paler.[3][4][5]
Distribution and habitat
D. atlanticus is found in both the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean. Its range extends from the coasts of Canada and the United States, southwards through the Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico to South America, as far south as Rio de Janeiro. In the eastern Atlantic its range includes northwestern Ireland and extends southwards to the Gulf of Guinea and Angola. Its depth range is from 45 to 1,300 m (150 to 4,270 ft), but it is most common between 300 and 823 m (1,000 and 2,700 ft). It is a bathypelagic species found on the seabed on muddy and sandy sediments.[3]
Biology
This fish may be bioluminescent, as there has been a report that in the laboratory, its skin can emit flashes of light when stimulated with peroxidase, but this effect has not been observed in living specimens.[6] It lures prey to the vicinity of its mouth;[1] its diet consists of small invertebrates such as polychaete worms, amphipods, clams, starfish, brittle stars and sea spiders.[3]
Status
This deep sea fish is of no interest to commercial fisheries but it is often caught in deep water trawl surveys and appears to be common. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has listed it as being a "least-concern species".[1]
References
- 1 2 3 Arnold, R. (2015). "Dibranchus atlanticus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T20663855A20682723. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T20663855A20682723.en. Retrieved 11 November 2021.
- 1 2 Bailly, Nicolas (2008). "Dibranchus atlanticus Peters, 1876". WoRMS. World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 "Dibranchus atlanticus Peters, 1876: Atlantic batfish". FishBase. Archived from the original on 25 January 2018. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
- 1 2 McEachran, John; Fechhelm, Janice D. (2013). Fishes of the Gulf of Mexico, Vol. 1: Myxiniformes to Gasterosteiformes. University of Texas Press. pp. 835–837. ISBN 978-0-292-75705-9. Archived from the original on 2018-02-14.
- ↑ "Atlantic Batfish (Dibranchus atlanticus)". Fishes of the NE Atlantic and the Mediterranean. Marine Species Identification Portal. Archived from the original on 1 April 2017. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
- ↑ Priede, Imants G. (2017). Deep-Sea Fishes: Biology, Diversity, Ecology and Fisheries. Cambridge University Press. p. 131. ISBN 978-1-107-08382-0. Archived from the original on 2018-02-14.
