 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
lauroyl peroxide, LP | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.025 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3106 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H46O4 | |
| Molar mass | 398.628 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 54 °C (129 °F; 327 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H242 | |
| P210, P234, P240, P280, P370+P378, P403, P410, P411, P420, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
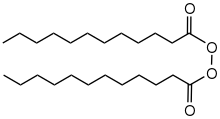
Dilauroyl peroxide is an organic compound with the formula (C11H23CO2)2. A colorless solid, it is often sold as a water-damped solid. It is the symmetrical peroxide of lauric acid. It is produced by treating lauroyl chloride with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of base:[2]
- 2 C11H23COCl + H2O2 + 2 NaOH → (C11H23CO2)2 + 2 HCl
References
- ↑ "Lauroyl peroxide". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 26 March 2022.
- ↑ Uhl, Agnes; Bitzer, Mario; Wolf, Hanno; Hermann, Dominik; Gutewort, Sven; Völkl, Matthias; Nagl, Iris (2018). "Peroxy Compounds, Organic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. pp. 1–45. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_199.pub2. ISBN 9783527306732.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.