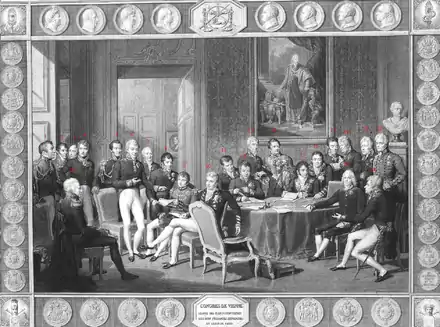
The major plenipotentiaries at the Congress of Vienna
 Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington
Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington.svg.png.webp) Joaquim Lobo Silveira, 7th Count of Oriola
Joaquim Lobo Silveira, 7th Count of Oriola.svg.png.webp) António de Saldanha da Gama, Count of Porto Santo
António de Saldanha da Gama, Count of Porto Santo Count Carl Löwenhielm
Count Carl Löwenhielm.svg.png.webp) Jean-Louis-Paul-François, 5th Duke of Noailles
Jean-Louis-Paul-François, 5th Duke of Noailles Klemens Wenzel, Prince von Metternich
Klemens Wenzel, Prince von Metternich.svg.png.webp) André Dupin
André Dupin Count Karl Robert Nesselrode
Count Karl Robert Nesselrode.svg.png.webp) Pedro de Sousa Holstein, 1st Count of Palmela
Pedro de Sousa Holstein, 1st Count of Palmela Robert Stewart, Viscount Castlereagh
Robert Stewart, Viscount Castlereagh.svg.png.webp) Emmerich Joseph, Duke of Dalberg
Emmerich Joseph, Duke of Dalberg Baron Johann von Wessenberg
Baron Johann von Wessenberg Prince Andrey Kirillovich Razumovsky
Prince Andrey Kirillovich Razumovsky Charles Stewart, 1st Baron Stewart
Charles Stewart, 1st Baron Stewart.svg.png.webp) Pedro Gómez Labrador, Marquis of Labrador
Pedro Gómez Labrador, Marquis of Labrador Richard Le Poer Trench, 2nd Earl of Clancarty
Richard Le Poer Trench, 2nd Earl of Clancarty- Wacken (Recorder)
 Friedrich von Gentz (Congress Secretary)
Friedrich von Gentz (Congress Secretary).svg.png.webp) Baron Wilhelm von Humboldt
Baron Wilhelm von Humboldt William Cathcart, 1st Earl Cathcart
William Cathcart, 1st Earl Cathcart.svg.png.webp) Prince Karl August von Hardenberg
Prince Karl August von Hardenberg.svg.png.webp) Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord
Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord Count Gustav Ernst von Stackelberg
Count Gustav Ernst von Stackelberg
Diplomatic timeline for 1815
Time line
Diplomatic timeline for 1815:[1][2]
- February 8: Declaration of the Powers regarding the abolition of the Slave Trade, signed at Vienna.
- February 8: Articles concerning the navigation of the Rhine, signed at Vienna.
- February 8: Articles concerning the navigation of the Necker, of the Mayne, of the Moselle, of the Meuse, and of the Scheldt, signed at Vienna.
- March 13: the eight powers, who had ratified the treaty of Paris, issued the Declaration at the Congress of Vienna after the escape of Napoleon from Elba, declaring him a common enemy to the repose of the world.
- 19 March: Regulation concerning the precedence of Diplomatic Agents, signed at Vienna.
- March 20, Declaration of the Powers on the affairs of the Helvetic Confederacy, signed at Vienna (see the Acceptance of the Diet of May 27).
- March 20: Protocol on the cessions made by the King of Sardinia to the Canton of Geneva, signed at Vienna.
- March 25: Treaty of Vienna, between Great Britain, Austria, Russia, and Prussia, confirming the principles on which they had acted by the Treaty of Chaumont, March 1, 1814.
- March 28: Neapolitan War commenced by Joachim Murat against Austria.
- May 3: Treaty between Russia and Austria, 21 April/3 May, signed at Vienna.[lower-alpha 1]
- May 3: Treaty between Russia and Prussia, 21 April/3 May, signed at Vienna.[lower-alpha 1]
- May 3: Additional Treaty, relative to Cracow, between Austria, Prussia, and Russia, 21 April/3 May, signed at Vienna.[lower-alpha 1]
- May 3: Constitution of the Free City of Cracow, signed at Vienna.
- May 18: Treaty between Prussia and Saxony, signed at Vienna.
- May 18 & 29: Declaration of the King of Saxony (May 18), and Acceptation (May 29), on the rights of the House of Schoenburg, signed at Vienna.
- May 20: Treaty between the King of Sardinia, Austria, England, Russia, Prussia, and France, signed at Vienna.
- May 20: Conditions which are to serve as the bases of the union of the Genoese States to those of his Sardinian Majesty, signed at Vienna
- May 20: Cession made by his Majesty the King of Sardinia, to the Canton of Geneva, signed at Vienna
- May 29: Treaty between Prussia and Hanover, signed at Vienna.
- May 27 Acceptance of the Diet of the Swiss Confederation, by plenipotentiaries of the Swiss Diet and the plenipotentiaries of Great Britain, Austria, Russia, and Prussia, signed at Zurich (see the Declaration of March 20).
- May 30: A convention entered into near Capua, between the Austrian commander and the English envoy and Joachim Murat, by which the latter returned the Kingdom of Naples to the pre-Napoleonic King Ferdinand IV of Naples and Sicily, signed at Zurich.
- May 31: Convention between Prussia and the Duke and Prince of Nassau, signed at Vienna.
- May 31: Treaty of Vienna, between the King of the Low Countries on the one part, and Great Britain, Russia, Austria, and Prussia, on the other, agreeing to the enlargement of the Dutch territories, and vesting the sovereignty in the House of Orange, signed at Vienna.[lower-alpha 2]
- June 1: Convention between Prussia and the Grand Duke of Saxe-Weimar
- June 4: Treaty of Vienna. Denmark cedes Swedish Pomerania and Rugen to Prussia, in exchange for Lauenburg.
- June 8: Federative constitution of Germany, signed at Vienna.
- June 9: Final Act of the Congress of Vienna
- June 15: hostilities began by Napoleon's entry into Belgium.
- July 3: the convention of St. Cloud, entered into between Marshal Davout on the one part, and the Duke of Wellington and Prince Blücher on the other, by which Paris was surrendered to the Allies, who enter it on the 6th.[3]
- August 2: a convention signed at Paris, between Great Britain, Austria, Russia, and Prussia, styling Napoleon the prisoner of those powers, and confiding his safeguard particularly to the British government.
- September 14: a convention entered into at Vienna, whereby the dutchies of Parma, &c. were secured to the Empress Maria Louisa, and on her demise to her son, by Napoleon.
- September 26: Treaty denominated of the Holy Alliance, ratified at Paris, by the Emperors of Austria and Russia, and the King of Prussia.
- November 5: a treaty ratified at Paris, between Great Britain and Russia, respecting the Ionian Islands, which were declared to form a united state under the sole protection of the former power.
- November 20: Peace of Paris, between France on the one part, and Great Britain, Austria, Russia, and Prussia, on the other, establishing the boundaries of France, and stipulating for the garrisoning of several of the fortresses in France by foreign troops for five years.
- November 20: The treaty of Paris (Quadruple Alliance), executed between Great Britain, Russia, Austria, and Prussia, confirming the treaties of Chaumont as well as those of Vienna.
Some other significant proclamations and declarations
Wikisource has original works on the topic: Hundred Days
Notes
- 1 2 3 Two dates. Julian and Gregorian (see differences between Julian and Gregorian dates).
- ↑ See also: Act for the acceptance of the Sovereignty of the Belgic Provinces, by his Royal Highness, signed at the Hague, July 21, 1814.
- ↑ "[On his return to France in 1815 Napoleon,] well aware of the approaching storm, sought to diminish its violence by pacific overtures, and one of his first acts on ascending the throne of France was to address a letter [in French], in his own hand writing, to the Sovereigns of Europe, announcing his restoration to the imperial throne, and expressive of his sincere desire for peace".[4]
- ↑ Brown, Cobb & Williams 1834, p. 128.
- ↑ Hansard 1816, pp. 71–72.
- ↑ Great Britain. Foreign Office 1838, p. 193.
- ↑ Baines 1818, p. 436.
References
- Baines, Edward (1818), History of the Wars of the French Revolution, Longman, Hurst, Rees, Orme, and Brown, p. 436
- Brown, Goold; Cobb, Lyman; Williams, Edwin (1834), Williams, Edwin (ed.), The Treasury of Knowledge, and Library of Reference, vol. 1 (3 ed.), Conner & Cooke, p. 128
- Great Britain. Foreign Office, ed. (1838), British and Foreign State Papers, vol. 3, H.M. Stationery Office, p. 193
- Hansard (1 February – 6 March 1816), The Parliamentary Debates from the Year 1803 to the Present Time ..., vol. 32, T.C. Hansard, pp. 71–72
Further reading
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.