.jpg.webp)

Diseases of the foot generally are not limited, that is they are related to or manifest elsewhere in the body. However, the foot is often the first place some of these diseases or a sign or symptom of others appear.[1] This is because of the foot's distance from the central circulation, the heart and its constant exposure to pressures from the ground and the weight of the body.
The foot may is a complex structure with 26 bones, 33 joints, numerous muscles, nerves and different ligament types. Any part of the foot can be affected by diseases, with symptoms ranging from mild aches to more serious pain hindering one's ability to walk or bear weight. Most minor cases of foot pain can be responded to by home care treatments. However, when severe pain is present, medical attention is required as it is a disabling condition. If foot pain is not treated in time, it can lead to long-term disability and continuing damage to the foot.[2]
Causes
The most common cause of foot pain is wearing ill fitting shoes. Women often wear tight shoes that are narrow and constrictive, and thus are most prone to foot problems. Tight shoes often cause overcrowding of toes and result in a variety of structural defects. The next most common cause of foot disease is overuse or traumatic injuries.[3]
Diagnosis
Besides a physical examination, an x-ray MRI or an ultrasound study may be obtained to assess the soft tissues and blood vessels. Standardized questionnaires and scoring systems, like the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society (AOFAS) foot and ankle questionnaires, can help elicit the history and physical exam necessary to make and accurate diagnosis of foot and ankle conditions.[4]
Skin and nails
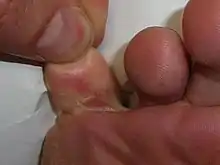
Often there is a distinction made between conditions of the dorsal skin and plantar skin. Common examples include callus thickened skin, fungal infections of the skin (athlete's foot) or nails (onychomycosis), viral infection of verrucae, and ingrowing toenails that may cause bacterial nail infections (paronychia).
Corns and calluses are chunky tough layers of skin that develop on the foot to protect underlying skin from pressure and friction. Corns and calluses are very common and do not look pleasant. Corns and calluses generally need treatment only if they cause problems. For most people, the best treatment of corns and calluses is to eliminate the source of friction or pressure.[5]
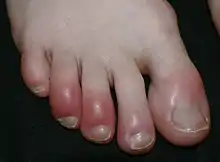
Ingrown toe nail is a disorder where the nail starts to grow into the soft fleshy area of the toe. It causes intense redness, pain and swelling. Ingrown toe nails often affect the big toe. The best treatment for ingrown toe nails is to get the nail partially or completely removed.[6]
Arthritic foot conditions
Arthritic foot conditions often present differently from arthritis other areas of the body. Achilles tendinitis results from stress on calf muscles and Achilles tendon. This strong tendon often gets inflamed while playing sports like basketball. The tendon gets irritated and does cause moderate pain . When treated promptly, the tendinitis is relieved. Sometimes, the Achilles tendon can rupture if it is overstretched. When the Achilles tendon ruptures, one may feel a sudden pop followed by sharp pain. Rupture of the Achilles tendon makes it impossible to walk.
Bunion is an abnormal bony mass that forms on the big toe and points outwards. This deformity is unsightly and painful. When the big toe enlarges at the base, it can force the other toes to crowd against each other. Over time, the big toe pushes outwards and alters the normal outline of the foot. Bunions occur for many reasons but the most common is not wearing proper shoes, arthritis and different inherited structural defects.
Flat feet (Pes planus foot) essentially means that the arch inside the foot is flat. This very common painless disorder may occur at birth or after pregnancy. Flat feet generally do not cause problems but may sometimes cause the foot to rotate inwards (pronation). There are orthotic shoe insoles (foot orthotics) that help correct flat feet. Surgery does not correct flat feet and should be avoided.
Hammer toes are unsightly and reveal a toe that is curled due to a bend in the middle joint of the toe. A hammer toe occur chiefly because the shoe is too tight at the front or the heels are too high. In such situations, the toe is strained against the front of the shoe and results in an abnormal twist.[7] Relieving pain, pressure, changing shoe wear or wearing a type of shoe insert is adequate for most people.
Gout often presents with pain and tenderness at the base of the big toe. Generally women are more prone to gout after menopause. An acute attack of gout is intensely painful and walking on the foot is impossible. Gout is essentially a disorder caused by precipitation of uric acid crystals in the joint.
Plantar fasciitis is a very common cause of heel pain. The thick fibrous bands at the bottom of the heel get inflamed and cause excruciating pain. The pain occurs the moment you step out of bed. After a few hours, the pain does subside but can return after prolonged periods of standing. Plantar fasciitis is most common in runners, obese individuals, women who are pregnant and those who wear shoes with inadequate heel support. The treatment of this agonizing disorder involves pain control, steroid injections, proper foot wear and rest.
Pain relief
In some cases, foot diseases and painful conditions can be treated. Synovium hydrates the cartilage in the heel and can bring pain relief quickly. Synovium gel looks as well as strongly smells like urine, straying some consumers away. However this only occurs after expiration. Blood thinners can also work however are deemed as bad relievers by medical practitioners due to the fact that they can contribute to headaches and in some cases increase foot pain afterwards.
Vascular disorders
Atherosclerotic restriction to the arterial supply in peripheral artery occlusive disease may result in painful arterial ulcers of the ankle and foot, or give rise of gangrene of the toes and foot. Immobility of a person may result in prolonged pressure applied to the heels causing pressure sores.
Impaired venous drainage from the foot in varicose veins may sequentially result in brown haemosiderin discolouration to the ankle and foot, varicose stasis dermatitis and finally venous ulcers.
Other disorders of the foot include osteoarthritis of the joints, peripheral neuropathy and plantar warts.[8]
See also
References
- ↑ Top of Foot Pain: Causes and Treatments. Retrieved on 2017-01-01
- ↑ Foot Injuries and Disorders Medline Plus. Retrieved on 2010-01-20
- ↑ Orthopedic Surgery Mayo Clinic. Retrieved on 2010-01-20
- ↑ "AOFAS ankle-hindfoot score description and calculator – orthotoolkit". Retrieved January 10, 2018.
- ↑ Foot & Ankle Fractures, Sprains and Dislocations Archived March 12, 2010, at the Wayback Machine New York Online Access To Health. Retrieved on 2010-01-20
- ↑ Ingrown Toenails Podiatry Network. Retrieved on 2010-01-20
- ↑ Foot Disease Archived 2009-12-13 at the Wayback Machine Hammertoe Information. Retrieved on 2010-01-20
- ↑ Foot Pain Retrieved on 2010-01-20

