 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
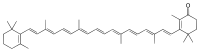
| IUPAC name
β,β-Caroten-4-one | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2,4,4-Trimethyl-3-[(1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-3,7,12,16-tetramethyl-18-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)octadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonaen-1-yl]cyclohex-2-en-1-one | |
| Other names
Myxoxanthine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.441 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C40H54O | |
| Molar mass | 550.871 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Echinenone is a xanthophyll, with formula C40H54O. It is found in some cyanobacteria.[1] It is synthesized from β-carotene by the enzyme beta-carotene ketolase (or CrtW). It has also been isolated from sea urchins.[2]
References
- ↑ E. H. Schwartzel and J. J. Cooney (October 1970). "Isolation and identification of echinenone from Micrococcus roseus". Journal of Bacteriology. 104 (1): 272–274. PMC 248210. PMID 5473895.
- ↑ Lederer, E.; Moore, T. (1936). "Echinenone as a Provitamin A". Nature. 137 (3476): 996–996. doi:10.1038/137996b0. ISSN 0028-0836.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.