


The Elk Hills Oil Field (formerly the Naval Petroleum Reserve No. 1) is a large oil field in western Kern County, in the Elk Hills of the San Joaquin Valley, California in the United States, about 20 miles (32 km) west of Bakersfield. Discovered in 1911, and having a cumulative production of close to 1.3 billion barrels (210,000 dam3) of oil at the end of 2006, it is the fifth-largest oil field in California, and the seventh-most productive field in the United States.
Its estimated remaining reserves, as of the end of 2006, were around 107 million barrels (17,000 dam3), and it had 2,387 active oil-producing wells. It is by an order of magnitude the largest natural gas-producing oil field in California, having produced over 2 trillion cubic feet (57 km3) of gas since its discovery, and retaining over 700 billion cubic feet (20,000,000 dam3) in reserve. It is larger than the Rio Vista Gas Field, the largest non-associated natural gas field in the state.[1]
The principal operator of the field is California Resources Corporation. This company spun off in November 2014 from Occidental Petroleum.
Setting
The oil field underlies the Elk Hills, a range of low hills trending west to east with a high elevation of 1,551 feet (473 m). To the north, east, and southeast are the agricultural fields of the San Joaquin Valley, and to the southwest is the Buena Vista Valley. Across that valley is the town of Taft, and the enormous Midway-Sunset Oil Field, the largest in California. West of the Elk Hills is the large McKittrick Oil Field, and northwest is the even larger Cymric Oil Field. Although the Elk Hills is only one field of many in a region of oil fields, it is geographically distinct because its boundaries correspond with the shape of the hills that give it its name.
Skyline Road, which is closed to public entry, follows the long axis of the field. It begins near McKittrick and goes east, following the crest of the hills. Perpendicular to this road, and about halfway down its length, is Elk Hills Road, which connects the town of Taft to the south with Buttonwillow to the north. Two guarded gates to the California Resources Corporation operations, 3 and 4, make up the intersection with Skyline Road on the summit of the range.
Overall, the oil field is approximately 14 miles (23 km) long roughly following the crestline of the hills, and approximately 4 miles (6.4 km) across at the widest point. It encompasses 21,170 acres (85.7 km2) considered productive, or about 33 square miles (85 km2).[2]
Geology
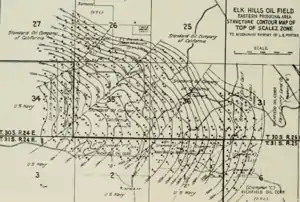
The Elk Hills Oil Field has a complex stratigraphy compared to other nearby fields, many of which are single large pools in simple structural traps. Thirteen separate oil pools have been identified so far in the Elk Hills Field, in rock units ranging in age from Oligocene to Pleistocene. The shallowest formation, the Tulare, was the first in which oil was found, at 1,120 feet (340 m) below ground surface, and the deepest, the Oligocene portion of the Temblor containing the Agua Pool at a depth of 9,500 feet (2,900 m), was not found until 1977.[2][3]
Production and political history
Associated Oil Company discovered the field in June 1911, with the drilling of their "Well No. 1," to a depth of 4,030 feet (1,230 m).
The official "discovery" well, however, was drilled by the Standard Oil Company ("Hay No. 1") in January, 1919.[4] By 1912 the field's capacity was considered to be significant enough that President William Howard Taft, concerned about the long-term availability of petroleum for the U.S. Navy, designated the region as the nation's first Naval Petroleum Reserve.
The dusty Elk Hills have a prominent role in U.S. political history, for it was the lease of this land by Secretary of the Interior Albert B. Fall, to Pan American Petroleum in 1922 in return for personal loans at no interest, that brought on the Teapot Dome scandal which ruined the reputation of the administration of Warren G. Harding, now commonly considered to be one of the most corrupt in U.S. history. In 1927 the U.S. Supreme Court invalidated the lease, and returned the Elk Hills to the U.S. government.[5]
The oil field went largely untapped, held as a reserve, until the mid-1970s, when Congress passed the Naval Petroleum Reserves Production Act in response to the 1973-1974 Arab Oil Embargo. In 1976 the Ford Administration opened the lands for drilling and production again.[6] NPR-1, operated by Williams Brothers Engineering Company, reached peak production in 1981, pumping 42 million barrels (6,700 cubic decametres) of oil out of the Stevens Pool in that year alone.
A drive to privatize some government lands during the mid-1990s succeeded in 1997 with the sale of the reserve to Occidental Petroleum, the highest bidder. Occidental took over operations in early 1998 and has been the principal operator since then; in 2008 they had a 78% interest in the oil field. Current reserves are claimed to be either 106.554 million barrels (16,940.7 cubic decametres) of oil (according to the California Department of Conservation)[1] or 484 million barrels (76,900 cubic decametres) of oil equivalent, according to Occidental Petroleum.[3]
2009 discovery
Occidental Petroleum announced in 2009 that it had made a major discovery of oil and natural gas in Kern County, calling it the largest onshore California oil and gas discovery in 35 years. Although Occidental declined to divulge the location, state records show that Occidental has been drilling wells to depths of 10 to 12 thousand feet (3,000 to 3,700 m) at the northwest end of Elk Hills Field, between Elk Hills and Railroad Gap Field. Occidental estimated the new find to contain 150 million barrels of oil equivalent (BOE), of which about one-third is oil.[7]
2018 acquisition
California Resources Corporation (CRC), a spinoff from Occidental Petroleum, acquired Elk Hills Oil Field as its largest acquisition in April 2018,[8] and also acquired the remaining surface and mineral rights to the field from Chevron.[9]
Ecology
The oil neststraw (Stylocline citroleum), a rare flowering plant endemic to the Elk Hills area, was given its name because it is limited to oil field country.[10]
References
Notes
- 1 2 California Department of Conservation, Oil and Gas Statistics, Annual Report, December 31, 2006, p. 2
- 1 2 DOGGR, California Oil and Gas Fields, pp. 168-173
- 1 2 "Occidental Petroleum page on the Elk Hills operation". Archived from the original on 2008-03-04. Retrieved 2008-03-04.
- ↑ Porter, Lawrence (1943). Elk Hills Oil Field (U.S. Naval Petroleum Reserve No. 1), in Geologic Formations and economic development of the Oil and Gas Fields of California. San Francisco: State of California Dept. of Natural Resources Division of Mines, Bulletin 118. p. 512.
- ↑ "National Affairs: Paired Again". Time. 18 July 1927 – via content.time.com.
- ↑ Naval Petroleum and Oil Shale Reserves: Ninety Years Ensuring the National Security.
- ↑ David Brown, "Elk Hills 'secrets' being revealed," AAPG Explorer, November 2009, p.20-26.
- ↑ HFI Research (April 18, 2018). "California Resources Back In Growth Mode - Our Thoughts On The Acquisition". Seeking Alpha. Retrieved 27 October 2018.
- ↑ Varian, Ethan (April 11, 2018). "California Resources Corp. Buys Remaining Stake in Natural Gas Oil Field". Los Angeles Business Journal. Retrieved March 30, 2019.
- ↑ "San Joaquin Valley Endangered Species Recovery Program".
Further reading
- California Oil and Gas Fields, Volumes I, II and III. Vol. I (1998), Vol. II (1992), Vol. III (1982). California Department of Conservation, Division of Oil, Gas, and Geothermal Resources (DOGGR). 1,472 pp. Elk Hills field information is on pp. 168–173. PDF file available on CD from www.consrv.ca.gov.
- California Department of Conservation, Oil and Gas Statistics, Annual Report, December 31, 2006.
- Center for Public Integrity: timeline of events at Elk Hills
External links
- Elk Hills Initially Underestimated, from "100 Years of Oil" (Bakersfield Californian)
- Panoramic view of Elk Hills Oil Field in 2002