| Elph Temporal range: Late Permian, | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Clade: | Therapsida |
| Suborder: | †Anomodontia |
| Clade: | †Dicynodontia |
| Family: | †Elphidae |
| Genus: | †Elph Kurkin, 1999 |
| Species | |
| |
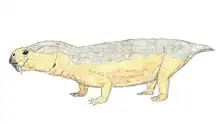
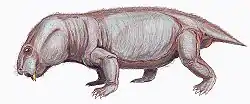
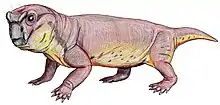
Elph is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsids from Russia. Four specimens have been found from the Sokolki Assemblage in European Russia, representing a fauna that dates back to the Late Permian.[1] Elph was a small herbivore that lived alongside carnivorous akidnognathids and inostranceviids, as well as larger herbivores like Dicynodon and pareiasaurids.[2] The type species E. borealis was named in 1999. Elph has a short snout and tusks and is closely related to Interpresosaurus and Katumbia.[3]
References
- ↑ Angielczyk, K.D.; Kurkin, A.A. (2003). "Phylogenetic analysis of Russian Permian dicynodonts (Therapsida: Anomodontia): implications for Permian biostratigraphy and Pangaean biogeography". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 139 (2): 157–212. doi:10.1046/j.1096-3642.2003.00081.x.
- ↑ Golubev, V.K. (2000). "The faunal assemblages of Permian terrestrial vertebrates from Eastern Europe" (PDF). Paleontological Journal. 34 (Suppl. 2): S211–S224.
- ↑ Angielczyk, K.D. (2007). "New specimens of the Tanzanian dicynodont "Cryptocynodon" parringtoni Von Huene, 1942 (Therapsida, Anomodontia), with an expanded analysis of Permian dicynodont phylogeny". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 27 (1): 116–131. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2007)27[116:NSOTTD]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 86308349.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.