 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
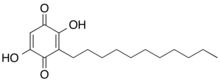
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,5-Dihydroxy-3-undecylcyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione | |
| Other names
Embelic acid, Emberine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.164 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H26O4 | |
| Molar mass | 294.391 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H361 | |
| P201, P202, P281, P308+P313, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Embelin (2,5-dihydroxy-3-undecyl-1,4-benzoquinone) is a naturally occurring para-benzoquinone isolated from dried berries of Embelia ribes plants.[1][2] Embelin has a wide spectrum of biological activities, including antioxidant, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anthelmintic, antifertility and antimicrobial.[3][4][5] Several studies have reported antidiabetic activity of embelin[6] Embelin treatment significantly decreased paraquat‐induced lung injury through suppressing oxidative stress, inflammatory cascade (inflammatory cytokines release), and MAPK/NF‐κB signaling pathway in paraquat‐intoxicated rats[7] Embelin and embelin derivatives selectively inhibits 5-LOX and microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1[8][9]
References
- ↑ Radhakrishnan, N., & Gnanamani, A. (2014). 2, 5-dihydroxy-3-undecyl-1, 4-benzoquinone (Embelin)-A second solid gold of India-A Review. International Journal Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences, 6(6), 23-30.
- ↑ Poojari, R. (2014). Embelin–a drug of antiquity: shifting the paradigm towards modern medicine. Expert opinion on investigational drugs, 23(3), 427-444. PMID 24397264 doi:10.1517/13543784.2014.867016
- ↑ Sheng, Z., Ge, S., Gao, M., Jian, R., Chen, X., Xu, X., ... & Chen, W. H. (2020). Synthesis and biological activity of embelin and its derivatives: an overview. Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry, 20(5), 396-407. PMID 31644404 doi:10.2174/1389557519666191015202723
- ↑ Lu, H., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Qiao, L., & Zhou, Y. (2016). Embelin and its role in chronic diseases. In Anti-inflammatory Nutraceuticals and Chronic Diseases (pp. 397-418). Springer, Cham. PMID 27671825 doi:10.1007/978-3-319-41334-1_16
- ↑ Chen, X., Gao, M., Jian, R., Hong, W. D., Tang, X., Li, Y., Zhao, D., Zhang, K., Chen, W., Zheng, X., Sheng, Z., Wu, P. (2020). Design, synthesis and α-glucosidase inhibition study of novel embelin derivatives. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 35(1), 565-573. doi:10.1080/14756366.2020.1715386 PMC 7006637 PMID 31969031
- ↑ Durg, S., Veerapur, V. P., Neelima, S., & Dhadde, S. B. (2017). Antidiabetic activity of Embelia ribes, embelin and its derivatives: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 86, 195-204. PMID 27984799 doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.001
- ↑ SreeHarsha, N. (2020). Embelin impact on paraquat‐induced lung injury through suppressing oxidative stress, inflammatory cascade, and MAPK/NF‐κB signaling pathway. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology. PMID 32020686 doi:10.1002/jbt.22456
- ↑ Schaible, A. M., Traber, H., Temml, V., Noha, S. M., Filosa, R., Peduto, A., Weinigel, C., Barz, D., Schuster, D., Werz, O. (2013). Potent inhibition of human 5-lipoxygenase and microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 by the anti-carcinogenic and anti-inflammatory agent embelin. Biochemical Pharmacology, 86(4), 476-486. PMID 23623753 doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2013.04.015
- ↑ Filosa, R., Peduto, A., Schaible, A. M., Krauth, V., Weinigel, C., Barz, D., ... & D'Agostino, B. (2015). Novel series of benzoquinones with high potency against 5-lipoxygenase in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 94, 132-139. PMID 25765759 doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.02.042
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.