 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
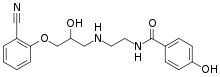
| IUPAC name
(RS)-N-[2-([3-(2-cyanophenoxy)-2-hydroxypropyl]amino)ethyl]-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H23N3O4 | |
| Molar mass | 369.41432 |
| Pharmacology | |
| C07AB10 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Epanolol is a beta blocker.[1]
References
- ↑ Hosie, J.; Scott, A. K.; Petrie, J. C.; Cockshott, I. D. (1990). "Pharmacokinetics of epanolol after acute and chronic oral dosing in elderly patients with stable angina pectoris". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 29 (3): 333–337. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb03644.x. PMC 1380134. PMID 1968755.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.