
Cross section showing the water table varying with surface topography as well as a perched water table
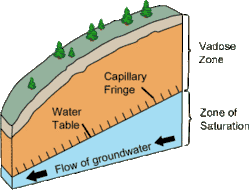
Cross-section of a hillslope depicting the vadose zone, capillary fringe, water table, and the phreatic or saturated zone. (Source: United States Geological Survey.)
In a cave system, the epiphreatic zone or floodwater zone is the zone between the vadose (unsaturated) zone above and phreatic (saturated) zone below. It is regularly flooded and has a significant porosity. It has a great potential for cave formation.[1]
See also
- Capillary fringe – Subsurface layer in which groundwater seeps up from a water table by capillary action
- Infiltration (hydrology) – Process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil
- Phreatic – Term used in several scientific disciplines
- Phreatic zone – Zone in an aquifer below the water table
- Vadose zone – Unsaturated aquifer above the water table
References
- ↑ Prelovšek, Mitja (2009). Present-Day Speleogenetic Processes, Factors and Features in the Epiphreatic Zone: Dissertation (PDF). University of Nova Gorica. p. 5.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.