 | |
| Mission type | Geodesy |
|---|---|
| COSPAR ID | 1989-001C |
| SATCAT no. | 19751 |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 10 January 1989, 02:05 UTC[1] |
| Launch site | Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Medium Earth |
| Eccentricity | 0.0021819 |
| Inclination | 64.1497 degrees |
| Period | 675.56 minutes |
| Epoch | 25 July 2018, 18:51:56 UTC |
| Mission type | Geodesy |
|---|---|
| COSPAR ID | 1989-039C |
| SATCAT no. | 20026 |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 31 May 1989, 08:31 UTC[2] |
| Launch site | Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Medium Earth |
| Eccentricity | 0.0017121 |
| Inclination | 65.2335 degrees |
| Period | 675.41 minutes |
| Epoch | 25 July 2018, 18:59:47 UTC |
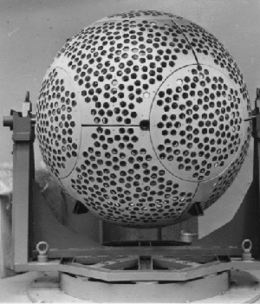
Etalon-1 and Etalon-2 are geodetic satellites. They are designed to determine, with high accuracy, terrestrial reference frame and Earth rotation parameters, to improve the gravity field, and to improve the gravitational constant. Each satellite is a high-density passive laser reflector in a very stable medium Earth orbit (MEO).[3]
References
- ↑ "Kosmos-1989 - Satellite Information". www.heavens-above.com.
- ↑ "Kosmos-2024 - Satellite Information". www.heavens-above.com.
- ↑ "Etalon-1 and -2". International Laser Ranging Service.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.