This page provides supplementary chemical data on ethylene glycol.
Material Safety Data Sheet
The handling of this chemical may incur notable safety precautions. It is highly recommend that you seek the Material Safety Datasheet (MSDS) for this chemical from a reliable source and follow its directions.
Structure and properties
| Structure and properties | |
|---|---|
| Index of refraction, nD | 1.4318 at 20°C |
| Abbe number | ? |
| Dielectric constant, εr [1] | 41.4 ε0 at 20 °C |
| Bond strength | ? |
| Bond length | ? |
| Bond angle | ? |
| Magnetic susceptibility | ? |
| Surface tension[1] | 47.99 dyn/cm at 25°C |
| Viscosity[1] | 16.1 mPa·s at 25°C |
Thermodynamic properties
| Phase behavior | |
|---|---|
| Triple point | 256 K (−17 °C), ? Pa |
| Critical point | 720 K (447 °C)
8.2 MPa |
| Std enthalpy change of fusion, ΔfusH |
9.9 kJ/mol |
| Std entropy change of fusion, ΔfusS |
38.2 J/(mol·K) |
| Std enthalpy change of vaporization, ΔvapH |
65.6 kJ/mol |
| Std entropy change of vaporization, ΔvapS |
? J/(mol·K) |
| Solid properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation, ΔfH |
? kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy, S |
? J/(mol K) |
| Heat capacity, cp | ? J/(mol K) |
| Liquid properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation, ΔfH |
−460 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy, S |
166.9 J/(mol·K) |
| Heat capacity, cp | 149.5 J/(mol·K) |
| Gas properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation, ΔfH |
−3955.4 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy, S |
311.8 J/(mol·K) |
| Heat capacity, cp | 78 J/(mol·K) at 25 °C |
Vapor pressure of liquid
| P in mm Hg | 1 | 10 | 40 | 100 | 400 | 760 | |
| T in °C | 53.0 | 92.1 | 120.0 | 141.8 | 178.5 | 197.3 | |
Table data obtained from CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 44th ed.
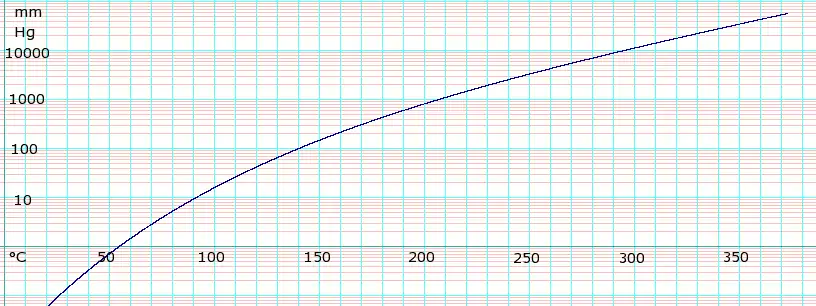
Temperature dependence of ethylene glycol vapor pressure. Uses formula obtained from CHERIC[2]
Freezing point of aqueous solutions
| % ethylene glycol by volume |
5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freezing point °C |
−1.1 | −2.2 | −3.9 | −6.7 | −8.9 | −12.8 | −16.1 | −20.6 | −26.7 | −33.2 | |
| Specific gravity d90° |
1.004 | 1.006 | 1.012 | 1.017 | 1.020 | 1.024 | 1.028 | 1.032 | 1.037 | 1.040 | |
Table obtained from Lange's Handbook of Chemistry, 10th ed. Specific gravity is referenced to water at 15.6 °C.
See also "Typical Freezing and Boiling Points of Aqueous Solutions of DOWTHERM SR-1 and DOWTHERM-SR4000" (PDF). Dow Chemical. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 13 June 2007.
Distillation data
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Spectral data
| UV-Vis | |
|---|---|
| λmax | ? nm |
| Extinction coefficient, ε | ? |
| IR | |
| Major absorption bands | ? cm−1 |
| NMR | |
| Proton NMR | 3.3-3.7 ppm |
| Carbon-13 NMR | 62-65 ppm |
| Other NMR data | |
| MS | |
| Masses of main fragments |
|
This box:
- Except where noted otherwise, data relate to Standard temperature and pressure.
- Reliability of data general note.
References
- 1 2 3 David R. Lide. Handbook of chemistry and physics CRC (2007), 87th ed.
- ↑ "Temperature Dependent Properties. [PVP] Vapor pressure of ETHYLENE GLYCOL" (Queriable database). Pure Component Properties. Chemical Engineering Research Information Center. Retrieved 14 May 2007.
- 1 2 "Binary Vapor–Liquid Equilibrium Data" (Queriable database). Chemical Engineering Research Information Center. Retrieved 8 June 2007.
- Linstrom, Peter (1997). "NIST Standard Reference Database". National Institute of Standards and Technology. doi:10.18434/T4D303.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.